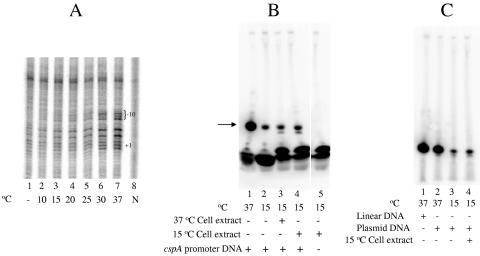
FIG. 5.
Promoter opening and transcription of cspA at a low temperature. (A) Temperature-dependent open complex formation by the cspA promoter. Promoter complexes were formed at indicated temperatures by using cspA promoter-containing fragments (both strands were 32P end labeled) and RNAP holoenzyme. Complexes were probed with KMnO4 and reaction products were separated by urea-PAGE and revealed by autoradiography. Lane 1 represents a reaction without RNAP at 37°C. Lane 8 (N) represents naked DNA without KMnO4 treatment. Positions of the −10 region and transcription start sites of cspA are indicated. (B) Low-temperature transcription of cspA in the presence of cell extract. Lanes 1 and 2 represent control reactions carried out at 37 and 15°C, respectively. Lanes 3 and 4 represent reactions carried out at 15°C in the presence of cell extract prepared at 37°C and 15°C, respectively. Lane 5 represents a control reaction carried out at 15°C in the presence of 15°C cell extract, without cspA promoter DNA. The position of the synthesized product is indicated by an arrow. (C) Effect of DNA supercoiling on low-temperature transcription of cspA. Abortive transcription initiation reactions were carried out by using linear or supercoiled DNA containing the cspA promoter. Lane 1 represents a control reaction carried out at 37°C using linear DNA. Lanes 2 through 4 represent reactions carried out by using supercoiled (plasmid-based) DNA containing the cspA promoter at the indicated temperatures. Cell extract prepared from cells cold shocked at 15°C for 1 h was included in the reaction represented in lane 4.