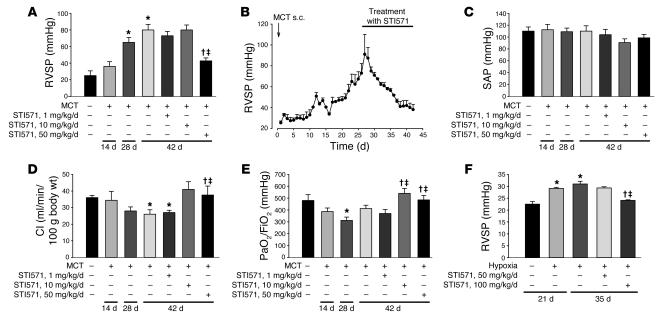
Figure 1.
Impact of STI571 treatment on hemodynamics and gas exchange in MCT- and hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. (A) RVSP (in mmHg) in the different treatment groups is shown. (B) Effect of STI571 on the course of RVSP in MCT-induced pulmonary hypertension measured by telemetry. MCT (s.c.) was applied at day 0 after animals had recovered from surgery for catheter implantation. Pulmonary hypertension developed progressively until day 28. STI571 was applied by daily i.p. injections at a dose of 50 mg/kg/d from day 28 to 42. In addition, systemic arterial pressure (SAP; in mmHg) (C), cardiac index (CI; in ml/min per 100 g body weight) (D), and oxygenation index (PaO2/FiO2) (E) are given for the different experimental groups. STI571 was applied at doses of 1, 10, and 50 mg/kg/d. (F) RVSP (in mmHg) in the different treatment groups of chronically hypoxic mice. STI571 was applied at doses of 50 and 100 mg/kg/d by gavage from day 21 to 35. *P < 0.05 versus control; †P < 0.05 versus MCT at day 28 or hypoxia at day 21; ‡P < 0.05 versus MCT at day 42 or hypoxia at day 35.