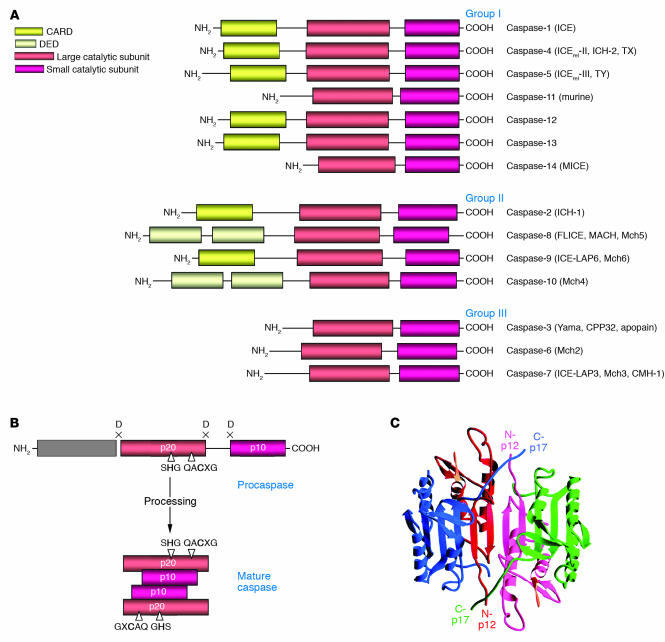
Figure 1.
Caspase structure. (A) The caspase family. Three major groups of caspases are presented. Group I: inflammatory caspases; group II: apoptosis initiator caspases; group III: apoptosis effector caspases. The CARD, the DED, and the large (p20) and small (p10) catalytic subunits are indicated. (B) Scheme of procaspase activation. Cleavage of the procaspase at the specific Asp-X bonds leads to the formation of the mature caspase, which comprises the heterotetramer p202–p102, and the release of the prodomain. The residues involved in the formation of the active center are shown. (C) The 3D structure of caspase-3 heterotetramer. Each heterodimer is formed by hydrophobic interactions resulting in the formation of mostly parallel β-sheets, composed of 6 antiparallel β-strands. Two heterodimers fit together with formation of a 12-stranded β-sheet that is sandwiched by α-helices. N and C termini of the small and large protease subunits are indicated.