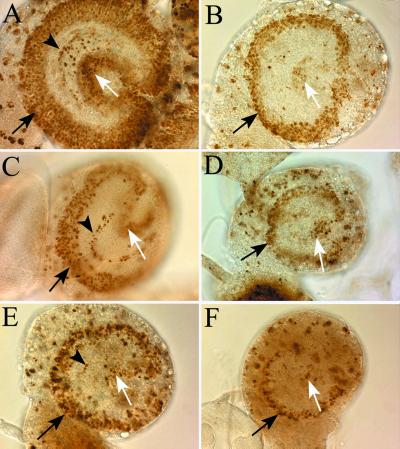
Figure 4.
DNA replication and cell proliferation are impaired in mutants of Pol γ. All panels depict photomicrographs of a lateral view of third instar larval brain hemispheres dissected from larvae that had incorporated BrdU to visualize mitotically active cells found in the developing adult optic lobes. All specimens were photographed at the same magnification. In all panels, the black arrow indicates the outer proliferation center, the arrowhead indicates the lamina precursor cells, and the white arrow indicates the inner proliferation center. Disruption of Pol γ function either by mutations in genes encoding the accessory subunit (B, C, and D) or the catalytic subunit (E and F) disrupts these proliferation centers to the same extent. (A) Wild-type CNS (pol γ-β1/+). (B) pol γ-β1 mutant CNS (pol γ-β1/Df(2L)b80c1). (C) Heteroallelic combination of two accessory-subunit mutant alleles (pol γ-β2/pol γ-β1). (D) pol γ-β2 mutant CNS (pol γ-β2/Df(2L)b80c1). Catalytic-subunit mutant CNS. (E) tam2/Df(2L)b80c1. (F) tam9/Df(2L)b80c1.