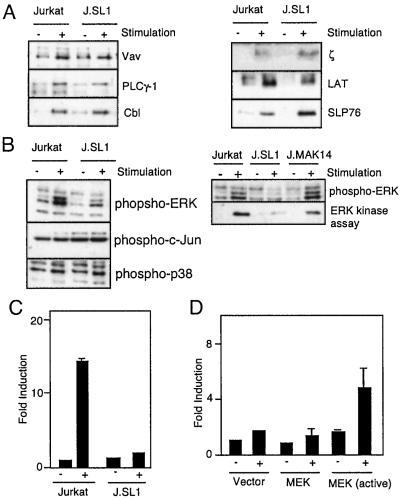
Figure 3.
MAPK activation is impaired in J.SL1 cells and is responsible for the loss of IL-2 production. (A) Tyrosine phosphorylation of signaling molecules in Jurkat and J.SL1 cells. Jurkat and J.SL1 cells were stimulated with anti-TCR antibody. Tyrosine phosphorylation of immunoprecipitated signaling molecules was determined by Western blot with anti-phosphotyrosine antibody. (B) Activation of MAPK (ERK1 and ERK2), c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38 by TCR in Jurkat, J.SL1, and J.MAK14 cells. Each cell line was stimulated by anti-TCR antibody. Total cell lysates were prepared at 5 min after stimulation. The lysates were analyzed (Left) by using Western blots with the antibody against phospho-MAPK (Top: ERK1, Upper; ERK2, Lower), phospho-c-Jun, and phospho-p38 (Bottom Left). J.MAK14 cells were also characterized (Right) for MAPK phosphorylation (Upper) and mitogen-activated protein kinase activity (Lower) by using Elk1 as the substrate for in vitro kinase assay of immunoprecipitated MAPK from each cell lysate. (C) Impaired IL-2 promoter activity in J.SL1 cells. Jurkat and J.SL1 cells were transfected with an IL-2 luciferase reporter construct. Each transfectant was stimulated (+) or nonstimulated (−) with anti-TCR antibody, and luciferase activity was determined 24 h later. Transfection efficiency was adjusted by using a dual reporter system (Promega). (D) Reconstitution of IL-2 promoter activity by expression of active MAPK in J.SL1 cells. J.SL1 cells were transfected with the expression construct for the activated MEK [MEK (active)], wild-type MEK (MEK), or the vector alone (Vector) with the IL-2 reporter construct. Sixteen hours after transfection, cells were not stimulated (−) or stimulated with anti-TCR antibody (+), and luciferase activity was determined 24 h after stimulation. Transfection efficiency was adjusted by using the dual reporter system.