Figure 6.
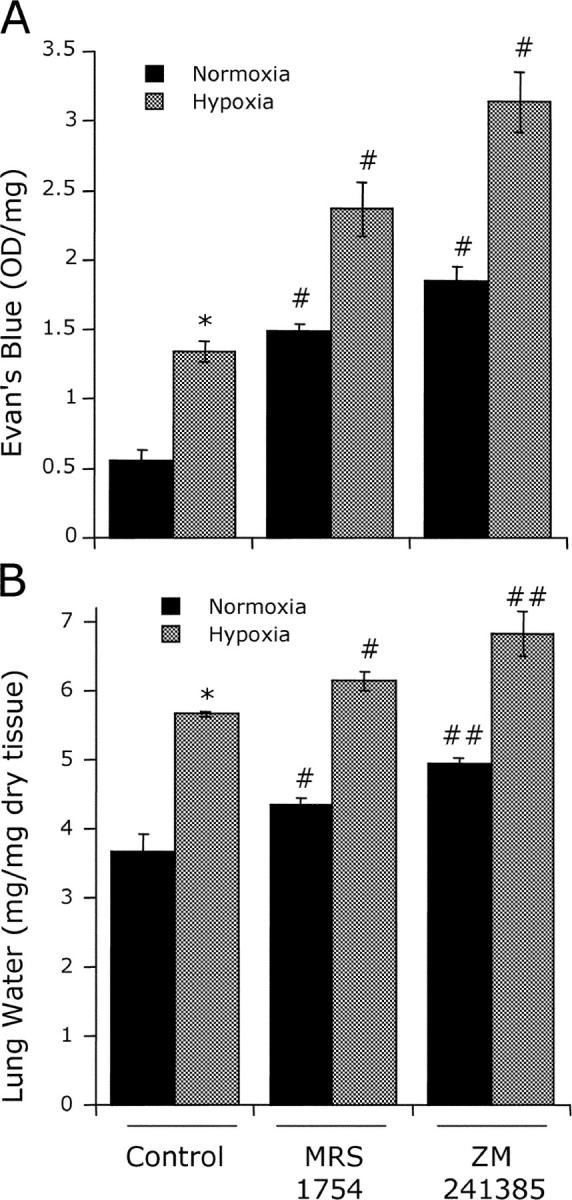
Influence of adenosine receptor antagonists on hypoxia-induced vascular leakage. Wild-type mice were administered either PBS (Control), the A2B receptor antagonist MRS1754 (1 mg/kg i.p. plus 1 mg/kg s.c.) or the A2A receptor antagonist ZM241385 (1 mg/kg i.p. plus 1 mg/kg s.c.) followed by intravenous Evan's blue solution (0.2 ml of 0.5% in PBS per mouse) and exposed to room air (black bars) or normobaric hypoxia (gray bars, 8% O2, 92% N2) for 4 h. Animals were killed, and lungs were harvested. (A) Evan's blue concentrations in organs were quantified as described in Materials and Methods. Data are expressed as mean ± SD Evan's blue OD/50 mg wet tissue and are pooled from four animals per condition where * indicates P < 0.01 between normoxia and hypoxia and # indicates P < 0.01 between treatment and control. (B) Assessment of lung water content. Data are expressed as mean ± SD mg H2O/mg dry tissue, and are pooled from four animals per condition where, in comparisons between hypoxia and normoxia, * indicates P < 0.01, # indicates P < 0.05 between treatment and control, and ## indicates P < 0.025 between treatment and control.
