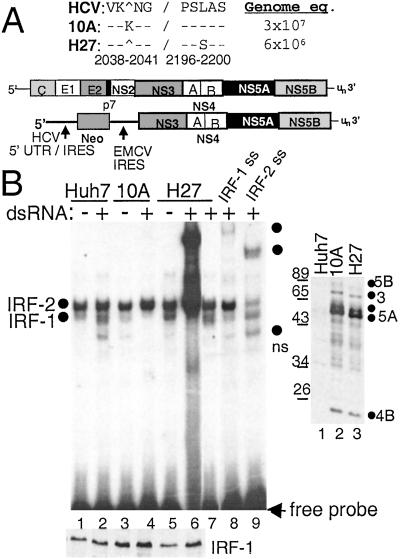
Figure 1.
Viral RNA replication efficiency and IRF-1 regulation of HCV replicon quasispecies. (A) Organization of the HCV genome and subgenomic replicon, with NS5A sequence variation between replicon clones 10A and H27. The amino acid positions are numbered according to the HCV 1b reference sequence, GenBank accession no. D11168. Replicon copy number is expressed as genome equivalents per micrograms of total cellular RNA. (B Right) Immunoblot analysis of HCV proteins in parental Huh7 cells (lane 1) or cells harboring replicon 10A (lane 2) or H27 (lane 3). The blot was probed with anti-HCV patient serum, and the positions of individual HCV proteins were identified by parallel comparison to identical blots that were probed separately with HCV protein-specific antisera. (B Left) Parental Huh-7 cells (lanes 1, 2, 8, and 9) or cells harboring replicon 10A (lanes 3 and 4) or H27 (lanes 5–7) were cultured for 2 h in the presence (+) or absence (−) of dsRNA. Nuclear extract (2 μg) was subjected to EMSA (Upper) or immunoblot analysis for IRF-1 protein levels (Lower). EMSA was conducted by using a probe encoding the ISRE of ISG54. Complexes were identified as IRF-1 or IRF-2 by supershift (ss) analysis of extracts from dsRNA-treated Huh7 cells by using Abs (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) to IRF-1 (lane 8) or IRF-2 (lane 9). Lane 7 shows the resolved complexes within a 10-fold dilution of the extract shown in lane 6. Dots indicate the probe-bound complexes. ns denotes a nonspecific complex not reproducibly observed. In B Upper entire gel is shown; all subsequent EMSA panels show only the region of the gel with probe-bound complexes.