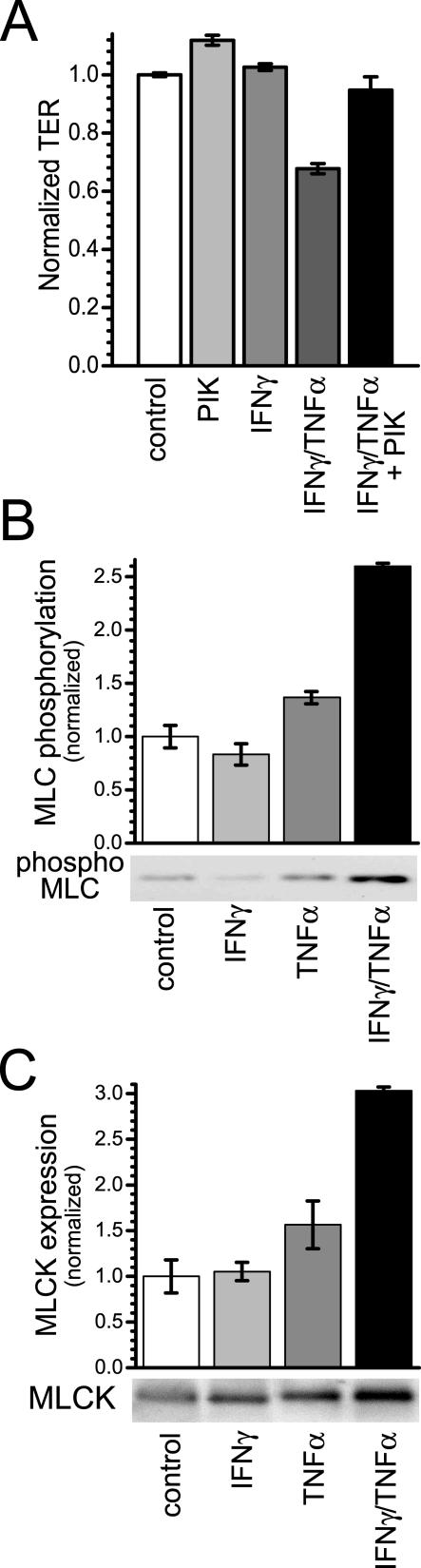
Figure 3.
IFN-γ- and TNF-α-dependent TER decreases are accompanied by increases in MLC phosphorylation and MLCK expression. A: Caco-2 monolayers were incubated in media with or without IFN-γ (10 ng/ml) for 24 hours and then transferred to media with or without TNF-α (2.5 ng/ml), as indicated. In the designated conditions, 200 μmol/L PIK, a highly specific membrane-permeant inhibitor of MLC kinase, was added to the apical media 2 hours after TNF-α addition. As we have shown previously,11 PIK alone induced a small increase in TER. However, in monolayers treated sequentially with IFN-γ and TNF-α, PIK was able to nearly completely prevent TER loss (P < 0.02) (n = 3 in this representative experiment). B: Caco-2 monolayers were incubated in media with or without IFN-γ (10 ng/ml) for 24 hours and then transferred to media with or without TNF-α (2.5 ng/ml), as indicated. Monolayers were harvested 8 hours after TNF-α addition. MLC phosphorylation was assessed by SDS-PAGE immunoblot. TNF-α (2.5 ng/ml) caused a small increase in MLC phosphorylation in monolayers without IFN-γ (10 ng/ml) pretreatment (P > 0.05), but a significant increase in MLC phosphorylation in cells with IFN-γ pretreatment (P < 0.05) (n = 2 in this representative experiment). C: Caco-2 monolayers were incubated in media with or without IFN-γ (10 ng/ml) for 24 hours and then transferred to media with or without TNF-α (2.5 ng/ml), as indicated. Monolayers were harvested 8 hours after TNF-α addition. MLCK protein expression was analyzed by SDS-PAGE immunoblot. TNF-α (2.5 ng/ml) caused a slight increase MLCK expression in monolayers without IFN-γ (10 ng/ml) pretreatment (P > 0.05), but a significant increase in MLCK expression occurred after TNF-α treatment of monolayers primed with IFN-γ (P < 0.05) (n = 2 in this representative experiment).