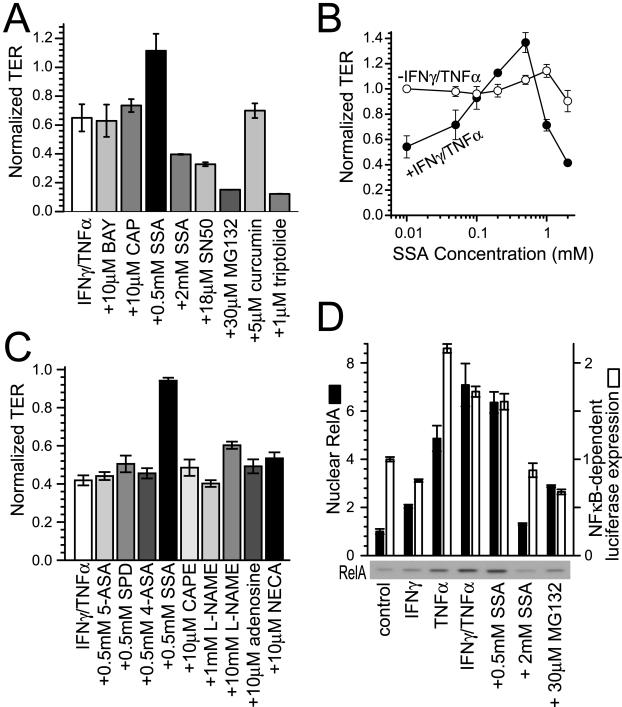
Figure 4.
Barrier defects induced by TNF-α and IFN-γ are not abrogated by NF-κB inhibition. A: Caco-2 monolayers were cultured with IFN-γ (10 ng/ml) for 24 hours and transferred to media with 10 μmol/L BAY 11-7085 (BAY), 10 μmol/L capsaicin (CAP), 0.5 mmol/L SSA, 2 mmol/L SSA, 18 μmol/L SN50, 30 μmol/L MG132, 5 μmol/L curcumin, or 1 μmol/L triptolide with or without TNF-α (2.5 ng/ml). None of the NF-κB inhibitors significantly altered TER without TNF-α treatment. TER of monolayers treated with TNF-α is normalized to identical monolayers, treated with the same NF-κB inhibitor, but without TNF-α. SSA (0.5 mmol/L) prevented TER decreases, but 2 mmol/L SSA, 18 μmol/L SN50, 30 μmol/L MG132, and 1 μmol/L triptolide exacerbated TER decreases. BAY 11-7085 (10 μmol/L), 10 μmol/L capsaicin, and 5 μmol/L curcumin had no significant effects (n = 3 in this representative experiment). B: Caco-2 monolayers were cultured with (closed circles) or without (open circles) IFN-γ (10 ng/ml) for 24 hours and transferred to TNF-α (2.5 ng/ml). SSA was also included at indicated doses (0.01 to 2 mmol/L). Maximal barrier protection occurred at 0.5 mmol/L. Higher SSA doses were not protective and, as shown in A, 2 mmol/L SSA exacerbated TER loss (n = 3 in this representative experiment). C: Caco-2 monolayers were cultured with IFN-γ (10 ng/ml) for 24 hours and transferred to TNF-α (2.5 ng/ml) with 0.5 mmol/L SSA, 0.5 mmol/L 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA), 0.5 mmol/L sulfapyridine (SPD), 0.5 mmol/L 4-aminosalicylic acid (4-ASA), 10 μmol/L caffeic acid phenethyl ester, 1 mmol/L and 10 mmol/L NG-nitro-l-arginine-methyl-ester (L-NAME), 10 μmol/L adenosine, and 10 μmol/L 5′-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (NECA). TER of monolayers treated with TNF-α is normalized to identical monolayers, treated with the same drug, but without TNF-α. Only SSA prevented barrier dysfunction induced by IFN-γ and TNF-α (n = 3 in this representative experiment). D: NF-κB RelA p65 (closed bars) was detected by SDS-PAGE immunoblot of nuclear fractions isolated 10 minutes after TNF-α (2.5 ng/ml) and drug addition to monolayers with or without IFN-γ (10 ng/ml) pretreatment for 24 hours, as indicated. A representative immunoblot of nuclear fractions is shown below the graph. NF-κB (RelA p65) nuclear translocation was inhibited by 2 mmol/L SSA and 30 μmol/L MG132, but not by 0.5 mmol/L SSA [n = 2 in this experiment which is representative of nine similar experiments, each with duplicate samples (total n = 18)]. NF-κB-dependent luciferase expression (open bars) was assessed in Caco-2 cells transiently transfected with pNFκB-TA-Luc reporter construct. Monolayers were then treated identically to the translocation assay, but harvested 8 hours after TNF-α addition to allow for luciferase synthesis. NF-κB-dependent luciferase expression was inhibited by 2 mmol/L SSA and 30 μmol/L MG132, but not by 0.5 mmol/L SSA [n = 2 in this experiment which is representative of four similar experiments, each with duplicate samples (total n = 8)].