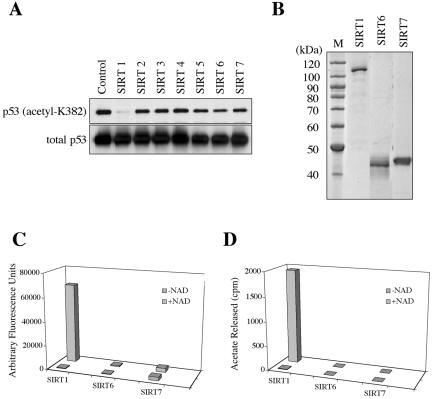
Figure 5.
Protein deacetylation assays of human SIRT proteins. (A) Cellular p53 protein was immunoprecipitated from control and the SIRT-overexpressing NHF cells, followed by Western blot analysis using anti-acetyl-K382p53 antibody (top panel) and anti-p53 antibody (DO-1, bottom panel). The amounts of K382-acetylated p53 were normalized with those of total p53 protein detected by DO-1. In three independent experiments (a representative result shown here), the SIRT1-overexpressing cells, but not any others, showed a significant decrease in the acetylated p53. (B) Recombinant SIRT1, SIRT6, and SIRT7 proteins were purified from the baculovirus-infected insect cells. One microgram of proteins were analyzed on a SDS-polyacrylamide gel. (C) The purified SIRT1, SIRT6, and SIRT7 proteins were examined for an in vitro deacetylase activity on the synthetic p53 peptide (amino acid residues 379–382). The reactions with and without NAD+ were included. (D) The purified SIRT1, SIRT6, and SIRT7 proteins were examined for an in vitro deacetylase activity on the histone H4 peptide (amino acid residues 2–24) in the presence or absence of NAD+.