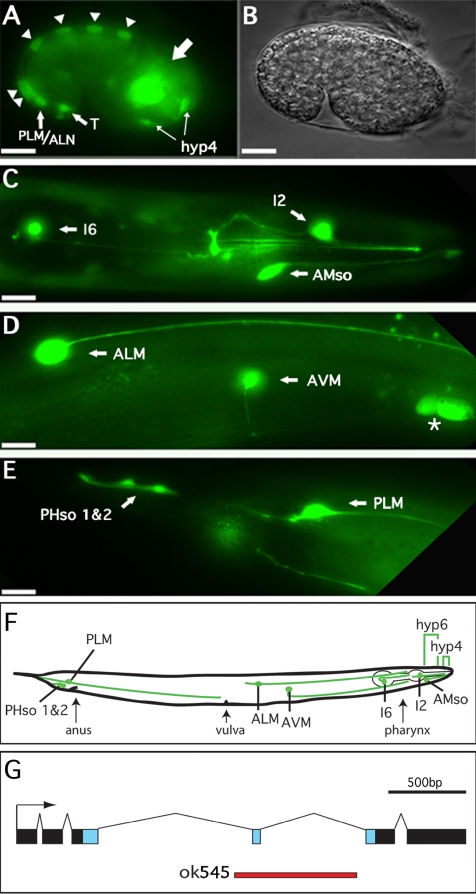
Figure 1.
alr-1p::GFP expression in embryonic and adult tissues. (A) Fluorescence and (B) differential interference contrast images of an alr-1p::GFP transgenic embryo at the late comma stage (400 min) showing expression in dorsal hypodermal cells (triangles), T-cells, PLM/ALM neurons, and hyp-4 precursor cells as well as unidentified cell bodies in the head region (large arrow). (C–E) Fluorescence images of alr-1p::GFP transgenic adults. (C) View of the head region revealing expression in the I6 and I2 neurons as well as the amphid socket cells (AMso). (D) Body midsection showing expression in the ALM and AVM neurons as well as nearby ceolomcytes (asterisk). (E) Tail of adult hermaphrodite with GFP expression in the PLM neurons as well as both of the phasmid socket cells (PHso 1 and 2). In all cases, partners of paired cells (left and right) expressed GFP, although they are not shown here because they are out of the plane of focus. (F) Schematic representation of an adult hermaphrodite indicating the relative positions of the alr-1::GFP-expressing cells. Brackets indicate the hyp6 and hyp4 hypodermal syncytia. Anterior is to the right, posterior to the left. Bars, 10 μm. (G) Exon/intron structure of alr-1. Blue boxes represent sequences encoding the homeodomain. The red line represents sequences deleted in alr-1(ok545).