Abstract
Transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ) signaling involves activation of a number of signaling pathways, several of which are controlled by phosphorylation events. Here, we describe a phosphoproteome profiling of MCF-7 human breast epithelial cells treated with TGFβ1. We identified 32 proteins that change their phosphorylation upon treatment with TGFβ1; 26 of these proteins are novel targets of TGFβ1. We show that Smad2 and Smad3 have different effects on the dynamics of TGFβ1-induced protein phosphorylation. The identified proteins belong to nine functional groups, e.g., proteins regulating RNA processing, cytoskeletal rearrangements, and proteasomal degradation. To evaluate the proteomics findings, we explored the functional importance of TGFβ1-dependent phosphorylation of one of the targets, i.e., transcription factor-II-I (TFII-I). We confirmed that TGFβ1 stimulated TFII-I phosphorylation at serine residues 371 and 743. Abrogation of the phosphorylation by replacement of Ser371 and Ser743 with alanine residues resulted in enhanced complex formation between TFII-I and Smad3, and enhanced cooperation between TFII-I and Smad3 in transcriptional regulation, as evaluated by a microarray-based measurement of expression of endogenous cyclin D2, cyclin D3, and E2F2 genes, and by a luciferase reporter assay. Thus, TGFβ1-dependent phosphorylation of TFII-I may modulate TGFβ signaling at the transcriptional level.
INTRODUCTION
Transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ) isoforms are members of a family of polypeptide growth factors that regulate embryonal development as well as normal and pathological processes in adult multicellular organisms (reviewed by Derynck et al., 2001; Chang et al., 2002; Wakefield and Roberts, 2002; Shi and Massagué, 2003). TGFβ binds to cell surface receptors with intrinsic serine/threonine kinase domains, and triggers activation of receptor kinases, followed by phosphorylation of cytoplasmic substrates. Genetic and molecular biological studies identified Smad proteins as crucial components of TGFβ signaling. TGFβ receptor-dependent phosphorylation of Smad2 and Smad3 is the triggering event for following interactions of Smad2 and Smad3 with different proteins, including the common mediator Smad4. Smad2- and Smad3-containing protein complexes are translocated to the nucleus, where they regulate gene expression. Despite structural homology, Smad2 and Smad3 show different activities in functional assays (Derynck et al., 2001; Piek et al., 2001; Chang et al., 2002; Wakefield and Roberts, 2002; Shi and Massagué, 2003). One of the explanations of such differences is the ability of Smad3 to bind DNA directly, whereas Smad2 interacts with gene promoters via other DNA-binding proteins (reviewed by Derynck et al., 2001; Wakefield and Roberts, 2002; Shi and Massagué, 2003). A number of Smad-independent pathways are also affected by TGFβ, e.g., mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases, phosphoinositide 3-kinase, and ion channels (Mulder, 2000; Wakefield and Roberts, 2002).
TGFβ has a dual role in tumorigenesis, inhibiting tumor growth at early stages and promoting tumorigenesis at later stages of cancer progression. Potent growth-inhibitory and proapoptotic activities of TGFβ contribute to suppression of tumor growth, whereas proangiogenic and immunosuppressive effects of TGFβ, as well as stimulation of tumor cell invasiveness, contribute to promotion of tumorigenesis (Derynck et al., 2001; Souchelnytskyi, 2002a; Wakefield and Roberts, 2002). Studies of selected signaling pathways or activities have provided insights into some mechanisms behind this dual role of TGFβ. However, a comprehensive analysis of the role of TGFβ in cancer should also include unbiased approaches, such as global proteome profiling.
Protein phosphorylation is one of the most important regulatory modifications, which occurs in signal transduction via several types of transmembrane receptors, as well as in several intracellular signaling pathways (Manning et al., 2002). Thus, global analysis of phosphorylation pattern is of crucial importance for the understanding of signaling processes. Development of methods for global phosphoproteome profiling is one of the major challenges of proteomics. Techniques using phospho-site-specific antibodies, chemical modifications of phosphorylated residues, immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC), and metabolic labeling of cells with radioactive [32P]orthophosphate have been used with various degree of success (Figeys, 2003; Patterson and Aebersold, 2003). Among these techniques, metabolic labeling with [32P]orthophosphate provides the most comprehensive and direct detection of phosphorylated proteins, compared with indirect detection with antibodies, purification of phosphoproteins and phosphopeptides by IMAC, or to purification of chemically modified phosphopeptides of proteins.
Here, we report a phosphoproteome profiling of TGFβ1-dependent protein phosphorylation in MCF-7 cells stably transfected with Flag-Smad2, myc-Smad3, or empty vector. Phosphoproteome profiling was performed using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, computer-assisted image analysis and matrix-assisted laser desorption-ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI TOF MS). We studied short- and long-term changes in protein phosphorylation, and we investigated the impact of increased expression levels of Smad2 and Smad3 on the phosphorylation. One of the identified targets, transcription factor-II-I (TFII-I), is known to facilitate interactions of the basal transcriptional machinery with specific transcription factors and is a convergence point for several signaling pathways in the regulation of transcription (Novina et al., 1998). Our data suggest that TGFβ1-induced phosphorylation of TFII-I modulates TGFβ1/Smad3-dependent transcriptional regulation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS0
Cells and Reagents
MCF-7 cells were obtained from American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA), and cells were cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% of fetal bovine serum (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO). To generate stably transfected cells, MCF-7 cells were transfected with empty pMEP4 vector (MCF-7-vector cells), Flag-Smad2 (MCF-7-Smad2 cells), or myc-Smad3 (MCF-7-Smad3 cells) in pMEP4 vectors. Transfected cells were selected by culturing cells in the presence of hygromycin. To generate cells stably expressing wild type or Ser371,743Ala mutant of TFII-I, MCF-7 cells were transfected with respective constructs and were selected in the presence of G418 (Geneticin).
Treatment of Cells
To induce expression of Flag-Smad2 and myc-Smad3, stably transfected MCF-7 cells were incubated with CdCl2 (5 μM) for 5 h. TGFβ1 (5 ng/ml) was added to cells 1, 4, or 24 h before lysis. Six hours before lysis, [32P]orthophosphate (0.1 mCi/ml; GE Healthcare, Uppsala, Sweden) was added to culture media. Cells were solubilized directly in the buffer for sample preparation.
Sample Preparation
Cells were lysed in 1% Triton X-100, 40 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 65 mM dithiothreitol (DTT), 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 10 mM aprotinin, and complete protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany). Lysates were clarified by centrifugation, and samples for two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2D-GE) were prepared using PlusOne 2D Clean-Up kit according to the manufacturer's recommendations (GE Healthcare). Samples were dissolved in buffer for 2D-GE (9.8 M urea, 2% CHAPS, 65 mM DTT, 0.5% IPG buffer, pH 3–10). Samples were aliquoted and stored at –70°C before use.
Two-dimensional Gel Electrophoresis
Samples (75 μg of protein) were subjected to isoelectric focusing (IEF) using IPGDry strips with immobilized pH gradient, pH range 3–10, 24 cm, linear (GE Healthcare). Samples were loaded by the in-gel rehydration technique, with active loading during the last 3 h. IEF was performed in an IPGphor (GE Healthcare) according to the following protocol: rehydration 10 h; 50 V, 3 h; 1000 V, 1 h; 8000 V, 10 h or to 50,000 Vh. After IEF, strips were equilibrated in 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.8, 6 M urea, 2% SDS, 30% glycerol with 1% DTT for 10 min, and then for 10 min in the same buffer without DTT but with 4% iodoacetamide. Equilibrated strips were placed on top of 12% polyacrylamide gels and fixed with 0.5% agarose in a concentrating buffer (62.5 mM Tris-HCl, pH 6.8, 0.1% SDS). The SDS-PAGE was performed in a Dalt-II (GE Healthcare), following the manufacturer's recommendations (constant power 100 W, run for 6–8 h). Gels were fixed in 10% acetic acid and 20% methanol for 10–12 h. Proteins were detected by silver staining as described previously (Shevchenko et al., 1996; Kanamoto et al., 2002). Gels were dried, and then they were exposed and scanned in a FujiX2000 PhosphorImager (Fuji, Tokyo, Japan). The pH gradient of the first-dimension electrophoresis was evaluated as proposed by the manufacturer of strips. Totally, 48 gels with samples from four experiments were prepared and subjected to analysis.
Gel Analysis
Silver-stained gels were scanned in an ImageScanner with the MagicScan32 software and analyzed by calculation of volumes of spots by the ImageMaster 2D Elite software (GE Healthcare). Radioactively labeled gels were exposed in a FujiX2000 PhosphorImager and scanned using the AIDA software (Raytest IMG, Sprockhoefel, Germany). Scanning files of gels were imported into the ImageMaster 2D Elite software, and images were analyzed. The linearity of data transfer from the PhosphorImager (AIDA software) to the ImageMaster 2D Elite software was controlled in separate experiments with various fixed amounts of radioactivity. Gels that did not show deviations in pattern of protein migration were used to generate master gels of the proteome of cells treated or not with TGFβ1. Normalization was performed to a total volume of radioactivity in all matched spots. Proteins changing their phosphorylation after treatment with TGFβ1 were considered for identification. Statistical significance of changes was evaluated using the ImageMaster 2D Elite software.
Protein Identification
TGFβ1-regulated protein spots were excised from the gels, destained, and subjected to in-gel digestion with trypsin (modified, sequence grade porcine; Promega, Madison, WI) as described previously (Hellman, 2000; Kanamoto et al., 2002). Tryptic peptides were concentrated and desalted on a “nano-column” (Gobom et al., 1999). Peptides were eluted with acetonitrile, containing the α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid as a matrix, and were applied directly onto the metal target and analyzed by MALDI TOF MS on a Bruker Autoflex (Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, Germany). Peptide spectra were internally calibrated using known autolytic peptides from trypsin. To identify proteins, we performed searches in the NCBInr sequence database using Mascot (www.matrixscience.com) and ProFound (http://65.219.84.5/service/prowl/profound.html) search engines. One miscut and partial oxidation of methionine were allowed. Probability of identification was evaluated according to the “P” value (Probability Based Mowse Score; for searches via Mascot), and according to probability value, “Z” value, and sequence coverage (for searches using ProFound). Correspondence of experimental values of pI and molecular mass of proteins to the theoretical values was also considered for identification.
Low-Density Microarray Experiment
Low-density microarray experiment was performed with RNA extracted from MCF-7 cells stably transfected with wild-type TFII-I and Ser371,743Ala mutant of TFII-I. Because pcDNA3 vector containing TFII-I constructs provides neomycin resistance, the cells were selected and cultured in the presence of G418. RNA was extracted using a RNAsy minikit (QIAGEN, Valencia, CA), and RNA without any signs of degradation was used. Preparation of probes (GEArray Probe synthesis kit, SuperArray Bioscience, Frederick, MD), and hybridization with membranes of a Human Cell Cycle Gene array (HS-001-4 GE array Q series; SuperArray Bioscience) were performed, as recommended by the manufacturer. Membranes after hybridization were exposed in a FujiX2000 PhosphorImager, and images were analyzed using the dedicated ScanAlyze software (SuperArray Bioscience).
Luciferase Reporter Assay
Reporter assays with CAGA(12)-luc, ARE-luc, and SRE-luc reporters were performed as described previously (Yakymovych et al., 2001). COS7 cells were used for this assay because they express relatively lower levels of TFII-I, compared with other cells. COS7 cells are responsive to treatment with TGFβ, albeit to a lower degree, compared with some other cells, e.g., Mv1Lu. 293T cells were used, because they are responsive to TGFβ and allow efficient expression of proteins.
Immunoprecipitation and Immunoblotting
Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting experiments were performed as described previously (Yakymovych et al., 2001). Cells were transfected and treated as indicated in the text.
DNA-Precipitation Assay
DNA-precipitation assay was performed with nuclear extracts from cells transiently transfected and treated as indicated in the text. Preparation of the CAGA(4x) probe, incubations of nuclear extracts, and electrophoresis were performed as described previously (Kurisaki et al., 2003).
Two-dimensional Phosphopeptide Mapping
MCF-7 or COS7 cells were treated as indicated in the text. Metabolic labeling of cells with [32P]orthophosphate (GE Healthcare) was performed as described previously (Yakymovych et al., 2001). Radioactively labeled TFII-I was subjected to digestion with trypsin (modified, sequence grade porcine; Promega), and the tryptic digest was separated on thin-layer cellulose plates by electrophoresis and chromatography as described previously (Yakymovych et al., 2001). Plates were exposed in a FLA-3000 PhosphorImager (Fuji), and images were analyzed. Phosphopeptides of interest were subjected to phosphoamino acid analysis and to Edman degradation, as described earlier (Yakymovych et al., 2001).
RESULTS
Phosphoproteome Profiling of TGFβ1 Signaling in MCF-7 Cells
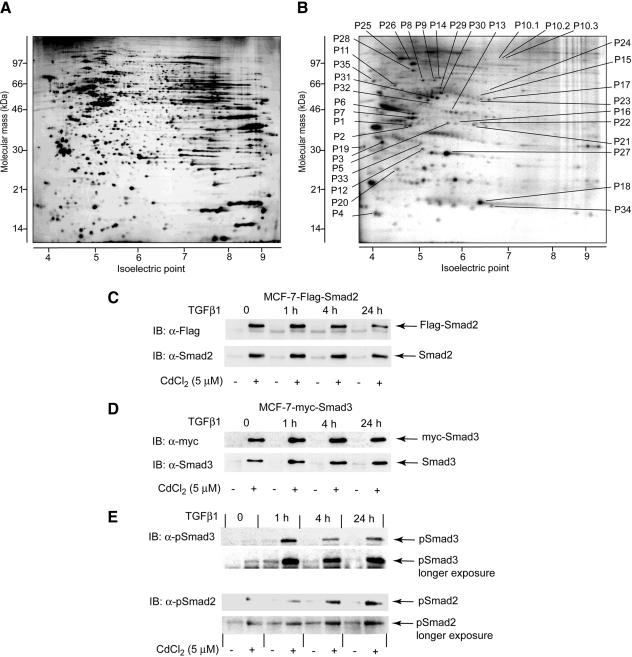
We explored changes in protein phosphorylation in MCF-7 cells stably transfected with inducible Flag-Smad2, myc-Smad3, or empty pMEP4 vector, in response to TGFβ1 stimulation (Figures 1, A and B, and 2; Table 1; and Supplemental Figures A and B). MCF-7 cells are often used as a model in studies of signaling in human breast epithelial cells, including TGFβ-dependent signaling, with >2000 publications referred in the MedLine. These publications suggest that processes studied in MCF-7 cells may be approximated to in vivo. To assess quick and long-term changes in protein phosphorylation, each of the cell lines was analyzed after incubation with TGFβ1 for 1, 4, and 24 h and was compared with nontreated cells. Expression of myc-Smad3 and Flag-Smad2 was induced by pretreatment of stably transfected cells with CdCl2; high levels of expression of Smad proteins were sustained during the time of treatment with TGFβ1 (Figure 1, C and D). myc-Smad3 and Flag-Smad2 were phosphorylated on their C-terminal serine residues upon TGFβ1 treatment, suggesting that the initiation of TGFβ signaling in stably transfected cells is not affected (Figure 1E). Samples from MCF-7 cells were subjected to 2D-GE; in an average 2D gel, we detected 1400 protein spots after silver staining. Silver-stained protein spots were distributed in all areas of the pH gradient (pH 3–10), and an approximately even distribution was found for proteins in the range of molecular masses from 14 to 100 kDa (Figure 1A). Four hundred forty-one phosphoprotein spots of 32P-labeled proteins were identified (Figure 1B). Most of the phosphorylated proteins were found in the part of the gel corresponding to pI values lower than 6.5, probably due to introduction of negative charges into protein molecules by phosphorylation. We found intergel variations for <8% of detected protein spots, suggesting a high reproducibility in generation of the 2D gels (Supplemental Figure A; our unpublished data).
Figure 1.
Two-dimensional maps of phosphorylated proteins in MCF-7 cells. Images of a silver-stained gel (A) and a gel with 32P-labeled proteins (B). Shown images are of gels that were obtained from vector-transfected MCF-7 cells nontreated with TGFβ1 (also see Supplemental Figure A for images of gels representative for all experimental conditions). Migration positions of spots containing proteins that changed phosphorylation level upon treatment with TGFβ1 cells transfected with the empty vector, Flag-Smad2, or myc-Smad, are shown. Annotation of spots and proteins that were identified in the spots by peptide mass fingerprinting, is the same as in Table 1. The pH gradient of the first-dimension electrophoresis is shown at the bottom of the gels. Migration positions of molecular mass markers for the second-dimension SDS-PAGE is shown on the side of the gels. P1 to P35 indicate migration positions of identified proteins. (C and D) Expression levels of Flag-Smad2 and myc-Smad3 in stably transfected cells were found to be sustained during the time cells were incubated with TGFβ1. Expression of Flag-Smad2 (C) was monitored by immunoblotting of total cells extracts with anti-Flag antibodies and antibodies to endogenous Smad2 protein. Expression of myc-Smad3 (D) was monitored by immunoblotting of total cell extracts with anti-myc antibodies and antibodies to endogenous Smad3 protein. (E) Phosphorylation of Smad2 and Smad3 was monitored by immunoblotting of total cell extracts with specific antibodies that recognize phosphorylated C-terminal serine residues in respective Smad proteins. C-terminal serine residues are phosphorylated by activated type I TGFβ receptor. Phosphorylation of endogenous Smad2 and Smad3 are indicated in panels with longer exposure. Expressions of total Smad2 and Smad3 proteins are shown in C and D. Cells were treated with TGFβ1 and preincubated with CdCl2 (5 μM), as indicated. Migration positions of Smad proteins are shown by arrows.
Figure 2.
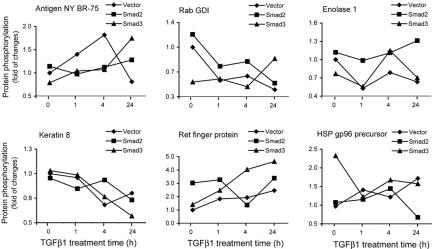
Clustering of phosphoproteins regulated by TGFβ1. Clustering of phosphorylated proteins according to an effect of the increased expressions of Flag-Smad2 or myc-Smad3. Five identified clusters are represented by phosphorylation profiles of breast cancer antigen NY-BR-75 (spot P22; group 1), RabGDI (spot P15; group 2), enolase 1 (spot P23; group 3), keratin 8 (spot P30; group 4), Ret finger protein (spot P16; group 5), and HSP gp96 precursor (spot P25; group 5). To calculate fold of changes, the radioactivity values of the same spot in various experimental conditions were compared with the radioactivity value of spot in the vector-transfected cells without TGFβ1 treatment. Radioactivity values are the average of four experiments. Average values of incorporated radioactivity and statistical significance of changes were calculated using the ImageMaster 2D Elite software. For annotation of proteins see Figure 1 and Table 1; phosphorylation profiles of all identified proteins are presented in Supplemental Figure B. Ret finger protein (spot P16) and HSP gp96 precursor (spot P25) represent the same cluster of proteins which showed phosphorylation patterns different in each of the cell types.
Table 1.
Identified proteins which change their phosphorylation upon TGFβ1 treatment
| Theoretical value
|
Experimental value
|
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No.a | Protein identityb | Accession no.b | Probabilityb | Estimated Zb | Sequence coverage, % | pI | Mr (kDa) | pI | Mr (kDa) |
| P1 | Eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1δ | AAH08012 | 1.0e+000 | 2.37 | 17 | 4.9 | 31.2 | 4.7 | 38 |
| P2 | Eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1δ | AAH08012 | 1.0e+000 | 2.43 | 22 | 5.0 | 31.3 | 4.8 | 38 |
| P3 | Eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1β | NP 001950 | 1.0e+000 | 1.68 | 20 | 4.5 | 24.9 | 4.2 | 32 |
| P4 | Acidic ribosomal phosphoprotein P2 | NP_000995 | 1.0e+000 | 2.40 | 71 | 4.4 | 11.7 | 4.1 | 17 |
| P5 | 60S ribosomal phosphoprotein P0 | NP_000993 | 1.0e+000 | 2.31 | 29 | 5.7 | 34.4 | 5.6 | 40 |
| P6 | Heterogenous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C (C1/C2) | AAH08423 | 1.0e+000 | 1.09 | 12 | 5.0 | 33.6 | 4.9 | 45 |
| P7 | Heterogenous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C (C1/C2) | AAH08364 | 1.0e+000 | 2.37 | 18 | 5.0 | 32.4 | 4.9 | 42 |
| P8 | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K | NP_112553 | 1.0e+000 | 2.35 | 32 | 5.1 | 51.3 | 5.0 | 80 |
| P9 | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K | NP_112553 | 1.0e+000 | 2.34 | 33 | 5.2 | 51.3 | 5.3 | 80 |
| P10.1 | General transcription factor II-I | NP_127494 | 5.4e-001 | 0.28 | 6 | 6.4–8.4 | 108–112 | 6.6 | 110 |
| P10.2 | General transcription factor II-I | NP_127494 | 1.0e+000 | 1.90 | 5 | 6.4–8.4 | 108–112 | 6.7 | 110 |
| P10.3 | General transcription factor II-I | NP_127494 | 1.0e+000 | 2.41 | 6 | 6.4–8.4 | 108–112 | 6.8 | 110 |
| P11 | RAD23 homolog B, HHR23B | NP_002865 | 1.0e+000 | 2.42 | 24 | 4.8 | 43.2 | 4.5 | 60 |
| P12 | Proteasome subunit, α type, 3 | NP_002779 | 1.0e+000 | 2.28 | 26 | 5.2 | 28.6 | 5.0 | 30 |
| P13 | 26S proteasome subunit p40.5 | NP_002808 | 1.0e+000 | 2.43 | 14 | 5.5 | 43.2 | 5.7 | 46 |
| P14 | Ras-GTPase-activating protein SH3-domain-binding protein | NP_005745 | 1.0e+000 | 2.39 | 21 | 5.4 | 52.2 | 5.4 | 80 |
| P15 | Rab GDP dissociation inhibitor, β | NP_001485 | 1.0e+000 | 2.34 | 29 | 5.9 | 51.1 | 6.2 | 55 |
| P16 | dJ25J6.4, Ret finger protein | CAB55434 | 9.7e-001 | 0.76 | 16 | 6.2 | 29.6 | 5.8 | 40 |
| P17 | Tumor necrosis factor α-induced protein 2 | XP_007258 | 5.5e-001 | 0.44 | 8 | 5.8 | 50.1 | 6.3 | 55 |
| P18 | Cofilin1 (nonmuscle) | NP_005498 | 1.0e+000 | 2.29 | 37 | 8.5 | 18.7 | 6.9 | 20 |
| P19 | Putative human HLA class II associated protein I | NP_006296 | 1.0e+000 | 1.25 | 19 | 4.0 | 28.7 | 3.8 | 30 |
| P20 | Melanoma antigen gp 75 | CAA35820 | 1.0e+000 | 1.68 | 20 | 4.7 | 28,5 | 4.6 | 27 |
| P21 | Serologically defined colon cancer antigen 28 | XP_035147.1 | 1.0e+000 | 2.28 | 34 | 6.7 | 33.4 | 6.2 | 40 |
| P22 | Serologically defined breast cancer antigen NY-BR-75 | AAG48263 | 6.0e-001 | 1.34 | 13 | 6.7 | 36.4 | 6.5 | 41 |
| P23 | Enolase 1 | NP_001419 | 1.0e+000 | 1.44 | 14 | 7.0 | 49.5 | 4.6 | 55 |
| P24 | Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase | 1QKIH | 1.0e+000 | 2.31 | 22 | 6.3 | 59.5 | 6.2 | 60 |
| P25 | HSP gp96 precursor | AAK74072 | 1.0e+000 | 2.34 | 20 | 4.7 | 90.4 | 4.5 | 120 |
| P26 | HSP 90-α (HSP86) | P07900 | 1.0e+000 | 1.96 | 18 | 4.9 | 85.1 | 4.7 | 100 |
| P27 | HSP 27 | NP_001531 | 1.0e+000 | 2.43 | 32 | 6.0 | 22.8 | 5.6 | 28 |
| P28 | BiP protein | AAF13605 | 1.0e+000 | 2.43 | 21 | 5.2 | 71.0 | 4.8 | 90 |
| P29 | Keratin, 67K type II cytoskeletal, human | A22940 | 1.0e+000 | 2.23 | 14 | 6.0 | 65.6 | 5.5 | 65 |
| P30 | Keratin 8, type II cytoskeletal | P05787 | 1.0e+000 | 2.38 | 28 | 5.5 | 53.7 | 5.5 | 60 |
| P31 | Keratin 10, type I, cytoskeletal | P13645 | 9.7e-001 | 1.51 | 14 | 5.2 | 59.8 | 5.4 | 55 |
| P32 | keratin 18, cytoskeletal, human (fragment) | S06889 | 1.0e+000 | 1.76 | 16 | 5.3 | 47.3 | 5.2 | 52 |
| P33 | Keratin-like protein, human (fragment) | I38025 | 1.0e+000 | 2.43 | 18 | 5.5 | 28.5 | 5.0 | 31 |
| P34 | Hypothetical protein | XP_002623 | 8.4e-001 | 0.44 | 8 | 7.1 | 16.1 | 6.6 | 17 |
| P35 | Hypothetical protein | XP_018191 | 1.0e+000 | 2.05 | 27 | 4.4 | 49.0 | 4.0 | 70 |
The calculation of experimental pI and Mr was based on migration of proteins on a 2D gel.
Selected protein spots from 32P-labeled gels
NCBInr sequence identification numbers. Probability, Z-value, coverage and theoretical pI and Mr were obtained from the ProFound search
Eighty-nine phosphoprotein spots, which showed TGFβ1-dependent differences in phosphorylation of >30% of incorporated radioactivity between at least two experimental conditions, were considered for identification; for example, if differences in protein phosphorylation were observed between experimental conditions corresponding to 0 and 1 h or between 0 and 4 h, or between 0 and 24 h, or between 4 and 24 h, or between 1 and 4 h, or between 1 and 24 h of TGFβ stimulation. After analysis of silver-stained gels, 47 phosphoprotein spots were selected for identification; the other 42 TGFβ1-regulated phosphoproteins were not suitable for mass spectrometry analysis because they were undetectable by silver staining or comigrated with abundant silver-stained spots. Selected protein spots were subjected to identification by peptide mass fingerprinting, as described in Materials and Methods. Ten of the selected phosphoprotein spots did not provide peptide spectra of high quality and will not be discussed. Thus, 32 proteins were identified with high confidence in 37 spots; some of the proteins were identified in multiple spots (Table 1).
Smad2 and Smad3 Have Different Effects on Protein Phosphorylation
In total, 111 phosphorylation profiles for identified proteins were obtained. We observed phosphorylations of the 32 proteins in a time- and/or Smad-dependent patterns that were specific for each protein (Figure 2 and Supplemental Figure B). Moreover, we observed an oscillating character of phosphorylation for many proteins.
We found that expression of Flag-Smad2 or myc-Smad3 strongly affected protein phosphorylation, compared with phosphorylation profiles of the same proteins in vector-transfected cells. Expression of Flag-Smad2 or myc-Smad3 would enhance Smad2- or Smad3-dependent phosphorylation of proteins upon treatment of cells with TGFβ. Different roles of Smad2 and Smad3 in transcriptional regulation have been shown (Piek et al., 2001), and our data indicate that Smads have also different effects on phosphorylation. We identified 5 groups of proteins, which differed with respect to how Smad expression affected their phosphorylation (Figure 2). The first group contains eleven proteins which were phosphorylated in vector-transfected cells with different time dependence than in Smad-transfected cells, whereas there were no pronounced differences between the same proteins from Flag-Smad2- and myc-Smad3-transfected cells (Figure 2, represented by breast cancer antigen NY BR-75, spot P22; Table 1, spots P2, P3, P4, P9, P17, P18, P22, P27, P28, P24, and P34; and Supplemental Figures B and C). The second group contains eight proteins with phosphorylation patterns similar for vector- and Flag-Smad2-transfected cells, but different for myc-Smad3-transfected cells (Figure 2, represented by Rab GDI, spot P15; Table 1, spots P7, P14, P15, P19, P20, P21, P32, and P35). The third group contains eight proteins with patterns of phosphorylation similar in vector- and myc-Smad3-transfected cells, but different in Flag-Smad2-transfected cells (Figure 2, represented by enolase-1, spot P23; and Table 1, spots P1, P5, P6, P29, P12, P23, P26, and P31). A fourth group contains two proteins that showed similar phosphorylation patterns in all three types of cells (Figure 2, represented by keratin 8, spot P30; and Table 1, ribonucleoprotein K, spot P8), and the fifth group consists of six proteins with phosphorylation patterns different in each of the cell types (Figure 2, represented by Ret finger protein, spot P16, and by HSP gp96 precursor, spot P25; Table 1, spots P10.1, P10.2, P10.3, P11, P13, P16, P25, and P33; and Supplemental Figures B and C). Thus, Smad2 and Smad3 affected TGFβ1-dependent protein phosphorylation of certain proteins differentially. This finding supports the notion that Smad2 and Smad3 have specific and various roles in transcriptional regulation and degradation processes (Piek et al., 2001; Shi and Massagué, 2003) and extends it to regulation of protein phosphorylation. The molecular mechanisms behind the effect of Smad2 and Smad3 on protein phosphorylation may be related to different interacting partners of these Smads and have to be explored further.
The identified proteins can be divided into nine groups according to their functions in cells. Six proteins that are components of the cytoskeleton or that regulate actin filament formation were identified (cofilin1, keratin 67K type II, keratin 8 type II, keratin 10 type I, keratin 18 and keratin-like protein; spots P18, P29, P30, P31, P32, and P33, respectively). Four proteins involved in protein translation form the second group (eukaryotic translation elongation factors 1δ and 1β, acidic ribosomal phosphoprotein P2 and 60S ribosomal phosphoprotein P0; spots P1, P2, P3, P4, and P5, respectively). Two other groups are formed by proteins regulating RNA processing (hnRNP C1/C2 and hnRNP K, identified in spots P6, P7, P8, and P9) and proteins with chaperoning functions (HSP gp96 precursor, HSP90 α, HSP27, and BiP, identified in spots P25, P26, P27, and P28). Three proteins involved in regulation of proteasomal degradation (Rad23 homolog B, proteasome subunit α3 and 26S proteasome subunit p40.5; spots P11, P12, and P13), and five proteins with functions in various signaling processes (TFII-I, Ras-GAP, Rab GDI, Ret finger protein and TNF-α-induced protein 2; spots P10, P14, P15, P16, and P17, respectively), were identified. Phosphorylation of enzymes regulating glycolysis (enolase 1, spot P23) and pentose cycle (glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase, spot P24) was found to be affected by TGFβ1. Three proteins that were identified as antigens (spots P20, P21, and P22) and HLA class II-associated protein I (spot P19) form the eighth group. The ninth group consists of two novel proteins with not yet attributed functional roles (spots P34 and P35). We did not observe common time-dependent changes for proteins within any of described functional groups. This is in agreement with various functional roles of phosphorylation, e.g., stimulatory or inhibitory. This also suggests that phosphorylation of every protein has to be explored in the context of its function.
We did not identify proteins known to change their phosphorylation upon TGFβ treatment, e.g., Smad2, Smad3, Erk kinase, or p38 kinase, despite that the phosphorylation of Smad2 and Smad3 was detectable in MCF-7 cells (Figure 1E; Fanayan et al., 2000; our unpublished data). Because we identified 32 proteins in 37 spots out of 89 protein spots that were regulated by TGFβ1, it is possible that some of the known targets are among the 52 nonidentified protein spots.
Six proteins out of the 32 identified have previously been reported to be affected by TGFβ. TGFβ1-dependent regulation of expression of keratin 10 type I, keratin 67K type II, and enolase 1 was described in Mv1Lu cells (Kanamoto et al., 2002). The levels of HSP27 and cofilin were found to be affected by TGFβ in fibroblasts (Bratt et al., 2001) and by glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase in human endothelial cells (Lomnytska et al., 2004). However, TGFβ-dependent phosphorylation of these six proteins has not been described. The other twenty-six identified proteins are novel targets of TGFβ1, which may provide insights into TGFβ regulation of cytoskeletal rearrangements, trafficking, proteasomal degradation and RNA processing (Table 1).
TFII-I Is Phosphorylated on Ser371 and Ser743 upon TGFβ1 Treatment of MCF-7 Cells
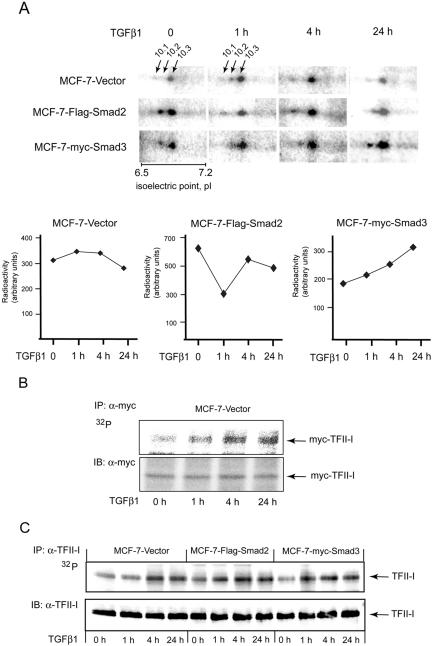
We selected one of the novel targets, transcription factor-II-I (TFII-I; spots P10.1, P10.2, and P10.3), for an exploration of the functional importance of the observed TGFβ1-dependent phosphorylation. TFII-I was identified in three phosphoprotein spots of similar molecular mass, suggesting at least three sites of phosphorylation of TFII-I (spots P10.1, P10.2, and P10.3; Figure 3A).
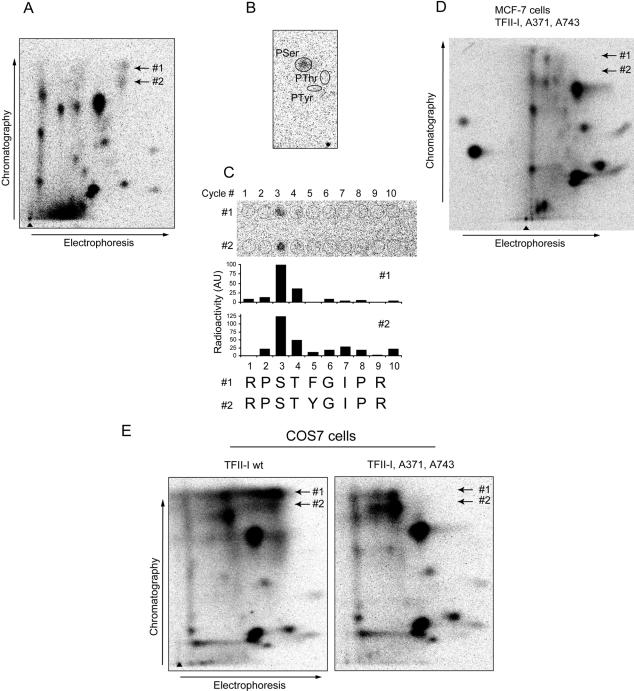
Figure 3.
TFII-I is phosphorylated upon treatment of cells with TGFβ1. (A) Phosphoprotein spots in which TFII-I was identified are shown in selected areas of images of gels with 32P-labeled proteins, which were prepared from MCF-7-vector, MCF-7-Flag-Smad2, and MCF7-myc-Smad3 cells. Migration positions of TFII-I-containing spots P10.1, P10.2, and P10.3 are indicated and are shown by arrows in two panels. Due to the presentation of gel images at similar intensities, borders for some of the software-designated spots may not be clearly recognized in panels. pH gradient is shown on the bottom of one of the images. Type of cells and time of treatment with TGFβ1 are shown on the side and on the top of the images, respectively. Quantification of total radioactivity in all three TFII-I-containing spots (summarized total activity in P10.1, P10.2, and P10.3 spots for one experimental condition) in cells treated with TGFβ1, or not, as indicted, is shown below the images. Note the difference in total radioactivity at 0-h time point. TGFβ1 treatment and cell lines are indicated. (B) Total phosphorylation of TFII-I was analyzed by immunoprecipitation of 32P-labeled myc-TFII-I with anti-myc antibodies. Phosphorylation of transfected myc-TFII-I in MCF-7-vector cells upon treatment of cells with TGFβ1 (5 ng/ml) for 1, 4, and 24 h is shown (top). Expression of myc-TFII-I was monitored by immunoblotting of the same membrane with anti-myc antibodies (B; bottom). (C) Phosphorylation of endogenous TFII-I in MCF-7-vector, MCF-7-Flag-Smad2, and MCF-7-myc-Smad3 cells was evaluated by immunoprecipitation of TFII-I with antibodies specific to endogenous protein from cells metabolically labeled with [32P]orthophosphate. Metabolic labeling of cells with [32P]orthophosphate was performed, as described in the Materials and Methods. Expression of myc-TFII-I was monitored by immunoblotting of the same membrane with anti-myc antibodies. Migration position of 32P-labeled and immunodetected myc-TFII-I are shown by arrows. Representative experiments out of three (B and C) performed are shown.
To confirm our findings, we transfected MCF-7 cells with a myc-TFII-I construct and investigated the effect of TGFβ1 on TFII-I phosphorylation (Figure 3B). We found that incubation of cells with TGFβ1, increased myc-TFII-I phosphorylation (Figure 3B). Phosphorylation of TFII-I was increased already after 1 h of TGFβ1 treatment of MCF-7-vector cells, compared with nontreated cells. TFII-I phosphorylation further increased after 4 h of treatment but then slightly decreased after 24 h of incubation of cells with TGFβ (Figure 3B).
We then further investigated phosphorylation of endogenous TFII-I. In accordance with the results obtained using proteomics technique, we observed that in vector-transfected cells TGFβ1 induced increase of phosphorylation already after 1 h and especially 4 h (2.1-fold, as strongest induction) of treatment, followed by slight decrease of phosphorylation after 24 h, compared with nontreated cells. TFII-I phosphorylation was increased in MCF-7-Flag-Smad2 cells even in absence of treatment with ligand to 1.3-fold, compared with vector-transfected nontreated cells (Figure 3C). Incubation of MCF-7-Flag-Smad2 cells with TGFβ resulted in further increase of TFII-I phosphorylation, although the fold of increase of TFII-I phosphorylation was relatively low (1.5-fold, as the strongest induction, and compared with nontreated cells). Incubation with TGFβ1 increased the phosphorylation of TFII-I in myc-Smad3-transfected cells as well, e.g., 1.87-fold after 1 h, 1.97-fold after 4 h, and 1.75-fold after 24 h, compared with nontreated cells (Figure 3C). Thus, we confirmed TGFβ- and Smad-dependent phosphorylation of TFII-I (Figure 3, B and C).
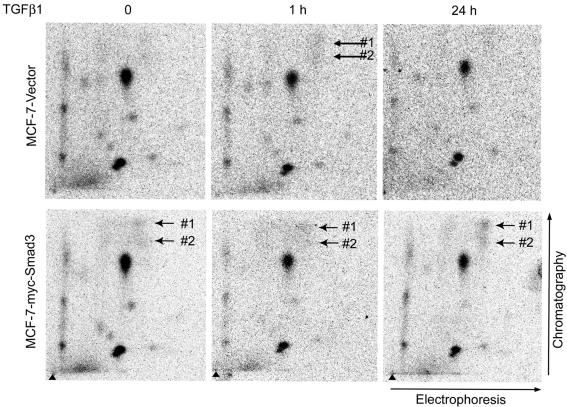
It should be noted that one-dimensional gel electrophoresis does not allow an efficient separation of TFII-I with various levels of phosphorylation, as was observed in 2D-GE. Under closer examination, two bands of endogenous TFII-I could be detected (Supplemental Figure D). The two bands may represent two isoforms of TFII-I (Cheriyath and Roy, 2000). Phosphopeptide mapping confirmed that these two bands represent the same protein; the maps of the two forms of the endogenous protein were identical to each other, and to the map of transfected TFII-I (Figures 4 and 5 and Supplemental Figure D).
Figure 4.
TGFβ1-induced appearance of two phosphopeptides in phosphopeptide maps of endogenous TFII-I. Endogenous TFII-I from vector-transfected MCF-7 cells or MCF-7-myc-Smad3 cells, which were treated or not with TGFβ1 (5 ng/ml), was subjected to two-dimensional phosphopeptide mapping. Arrows show migration position of phosphopeptides that occurred after treatment of cells with TGFβ1. Triangles show sample application points. Directions of electrophoresis and chromatography are shown at the sides of the maps. Cell lines are indicated at the side of the maps, and time of treatment of cells with TGFβ1 is indicated on the top of the maps. Representative maps out of three performed experiments are shown.
Figure 5.
TFII-I is phosphorylated at serine residues 371 and 743 upon treatment of cells with TGFβ1. (A) Two TGFβ1-induced phosphopeptides, #1 and #2, were identified in a phosphopeptide map of transfected myc-TFII-I that was immunoprecipitated from MCF7-vector cells metabolically labeled with [32P]orthophosphate. Cells were treated with TGFβ1 (5 ng/ml) for 4 h. Migration positions of the peptides are shown by arrows. (B) The phosphopeptides shown in A were eluted and subjected to phosphoamino acid analysis. For both peptides, radioactivity was comigrating with phospho-serine (pSer), and no radioactivity was comigrating with phospho-threonine (pThr) or phospho-tyrosine (pTyr). Migration positions of pSer, pThr, and pTyr are indicated. (C) Radioactivities in both TGFβ1-dependent phosphopeptides were released in the third cycle of radiochemical sequencing (C; top). Localizations of applied fractions are shown by open cycles, and number of cycles is shown (top). Quantification of the signals presented (top of panels) is shown (middle). Cycles of radiochemical degradation are aligned with sequences of two candidate peptides (C; bottom). (D) Phosphopeptide mapping of myc-TFII-I with serine residues 371 and 743 replaced by alanine residues did not show phosphopeptides #1 and #2. TFII-I mutant Ser371,743Ala was transfected in MCF-7 cells, and metabolic labeling, immunoprecipitation, and phosphopeptide mapping were performed as for wild-type myc-TFII-I. Expected migration positions for phosphopeptides #1 and #2 are shown by arrows. (E) Mutation of serine residues 371 and 743 abrogated appearance of two phosphopeptides migrating at identical positions as TGFβ1-dependent phosphopeptides, in myc-TFII-I expressed in COS7 cells. Cells transfected with wild-type or mutant myc-TFII-I were metabolically labeled with [32P]orthophosphate and were incubated with 8-Br-cGMP to activate cotransfected PKG. myc-TFII-I was immunoprecipitated with anti-tag antibodies, and phosphopeptide mapping was performed. Migration positions of phosphopeptides #1 and #2 are shown by arrows.
To identify the sites of TGFβ1-dependent phosphorylation of TFII-I, we performed phosphopeptide mapping of TFII-I (Figure 4). We analyzed both phosphoprotein bands which were observed in the 1D gel (Figure 3C). Phosphopeptide maps of both endogenous proteins and phosphopeptide maps of TFII-I expressed in MCF-7 or COS7 cells were identical, strongly suggesting that this is the same protein (Figures 4 and 5 and Supplemental Figure D). We found multiple phosphorylation sites in TFII-I in the basal state; this is in agreement with the reported role of TFII-I as a convergence point for multiple kinases in regulation of transcription (Kim et al., 1998; Novina et al., 1998; Kim and Cochran, 2000; Egloff and Desiderio, 2001; Kim and Cochran, 2001; Roy, 2001,Casteel et al., 2002; Cheriyath et al., 2002). We found that treatment of cells with TGFβ1 led to appearance of two new phosphopeptides (Figure 4). These phosphopeptides were also observed in maps of TFII-I obtained from Flag-Smad2- or myc-Smad3-tansfected cells, even if the cells were not treated with TGFβ1 (Figure 4; our unpublished data). Thus, the appearance of new phosphopeptides correlated with the pattern of TFII-I phosphorylation, which was observed in 2D gels.
To identify the sites of phosphorylation of TFII-I, the TGFβ1-dependent phosphopeptides were eluted from the plates and subjected to phosphoamino acid analysis and radiochemical sequencing using Edman degradation (Figure 5, A–C). We found that both phosphopeptides contained phosphoserine residues, which were located at position three (Figure 5, B and C). In silico digestion of TFII-I with trypsin predicted nine peptides with a serine residue at the third position (Supplemental Figure E). The predicted migration of potential candidates in 2D phosphopeptide maps, suggested that peptides containing Ser371 and Ser743 best corresponded to the observed phosphopeptides. These two peptides have similar sequences and differ only by one amino acid residue (Figure 5C); the presence of a tyrosine residue versus a phenylalanine residue may explain the slight difference in migration of the peptides in chromatography, and almost identical migration in electrophoresis (Figure 5A). We transfected TFII-I constructs with the serine residues 371 and 743 mutated to alanine residues into MCF-7 cells and performed phosphopeptide mapping of TFII-I; as predicted, the TGFβ1-dependent phosphopeptides were not detected in the maps of the Ser371,743Ala mutant of TFII-I (Figure 5D). We also confirmed phosphorylation at Ser371 and Ser743 of TFII-I expressed in COS7 cells, which were used for functional evaluation of TFII-I phosphorylation (Figure 5E). Thus, we have identified Ser371 and Ser743 in TFII-I as sites of TGFβ1-induced phosphorylation.
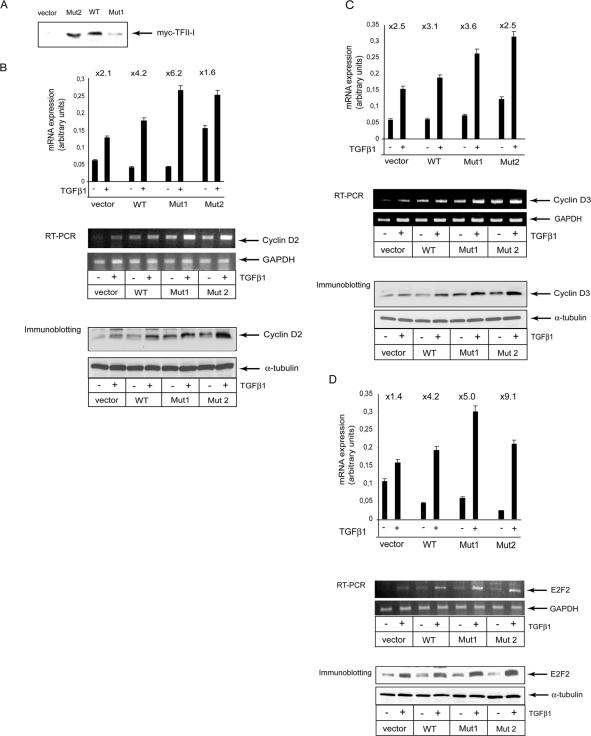
Abrogation of TFII-I Phosphorylation on Ser371 and Ser743 Affects TGFβ1-dependent Regulation of Cyclin D2, Cyclin D3, and E2F2 Gene Expression
TFII-I is a unique transcription factor because it provides a link between the basal transcriptional machinery and specific transcription factors (Roy, 2001). To explore whether phosphorylation of TFII-I affects transcriptional responses to TGFβ1, we performed a low-density microarray analysis of MCF-7 cells stably transfected with wild-type and mutated TFII-I and treated or not with TGFβ1. We used two cell clones for the phosphorylation-deficient mutant of TFII-I, one with the high level and the second with the low level of TFII-I expression (Figure 6A). Human Cell Cycle Gene Array Q series allows evaluation of expression of 96 genes involved in the cell cycle regulation and response to DNA damage. We found that expressions of mRNA of cyclin D2, cyclin D3, and E2F2 were regulated in a TFII-I-dependent manner (Figure 6, B–D, top). TGFβ1 increased expression of these three genes, and transfection of wild-type TFII-I enhanced the effect of TGFβ1. Transfection of MCF-7 cells with the Ser371,743,Ala TFII-I mutant resulted in an enhancement of cyclin D2, cyclin D3, and E2F2 gene expression, compared with cells transfected with wild-type TFII-I (Figure 6, B–D). The higher expression level of mutated TFII-I (Mut 2) also led to ligand-independent increase in transcriptional activation of cyclin D2 and cyclin D3 genes, compared with cells expressing mutated TFII-I at the lower level. This is in agreement with the role of TFII-I phosphorylation in regulation of these genes. The basal level of E2F2 expression in cells transfected with mutant TFII-I at high level was lower, compared with other cells. However, the induction after TGFβ1 stimulation was almost twofold higher, compared with cells transfected with wild-type TFII-I (Figure 6D). Microarray data were confirmed using reverse transcription (RT)-PCR with specific primers (Figure 6, B–D, middle). Moreover, the similar pattern of regulation by TGFβ and TFII-I expression was observed for cyclin D2, cyclin D3, and E2F2 proteins, as evaluated by immunoblotting with specific antibodies (Figure 6, B-D, bottom). Microarray, RT-PCR and immunoblotting experiments clearly indicate that TFII-I and its phosphorylation at Ser371 and Ser 743 modulate TGFβ-dependent expression of selected genes (Figure 6, B-D).
Figure 6.
Abrogation of TGFβ1-dependent phosphorylation of TFII-I at Ser371 and Ser743 increased TGFβ1-dependent induction of cyclin D2, cyclin D3, and E2F2 genes. (A) MCF-7 cells were stably transfected with wild-type (WT), or Ser371,743Ala mutant (Mut1 and Mut2) of myc-TFII-I, or with empty pcDNA3 vector. Migration position of immunoprecipitated and immunoblotted myc-TFII-I constructs is indicated by an arrow. Stably transfected cells were treated with TGFβ1 (5 ng/ml) for 12 h, and total RNA was extracted and labeled and used for hybridization with membranes of a human cell cycle gene array HS-001. Membranes were exposed in a PhosphorImager, and obtained images were analyzed with a dedicated software. Regulation of expression of mRNA of cyclin D2 (B), cyclin D3 (C), and E2F2 (D) (top). Cells were treated as indicated. Fold of TGFβ1-dependent induction for each of the conditions is indicated on the top of panels. Each gene was represented in four spots in the arrays, and average values were calculated. Validation of microarray data by RT-PCR is shown (middle) (B–D). Specific bands for cyclin D2, cyclin D3, and E2F2 and control GAPDH bands are indicated by arrows. Validation of microarray data by immunoblotting for cyclin D2, cyclin D3, and E2F2 proteins is shown (bottom) (B–D). Loading control by immunoblotting of the same membrane with anti α-tubulin antibodies is shown. Representative experiments out of two performed with four repeats in each (for microarray), of three for RT-PCR, and five for immunoblotting, are shown.
Importantly, we found that TGFβ1-dependent regulation of a number of other genes was not affected by transfection of TFII-I wild-type or mutant (Supplemental Figures F and G). We found also that TGFβ1 regulated in the stably transfected cells its known target genes, e.g., cyclin D1, cyclin F, cyclin G2, cdc2, cdk2, E2F2, E2F3, and GADD45A (Supplemental Figure G). This suggests that TFII-I modulates TGFβ1-dependent transcriptional regulation selectively and does not have a general effect. It also suggests that initiation of the TGFβ signaling pathway, at least on the level of receptors and Smad activation, is not affected by transfection of wild-type or mutant TFII-I. Thus, we found that substitution of the phosphorylatable serine residues 371 and 743 in TFII-I to alanine residues, modulated TGFβ1-dependent transcription of endogenous cyclin D2, cyclin D3, and E2F2 genes in MCF-7 cells.
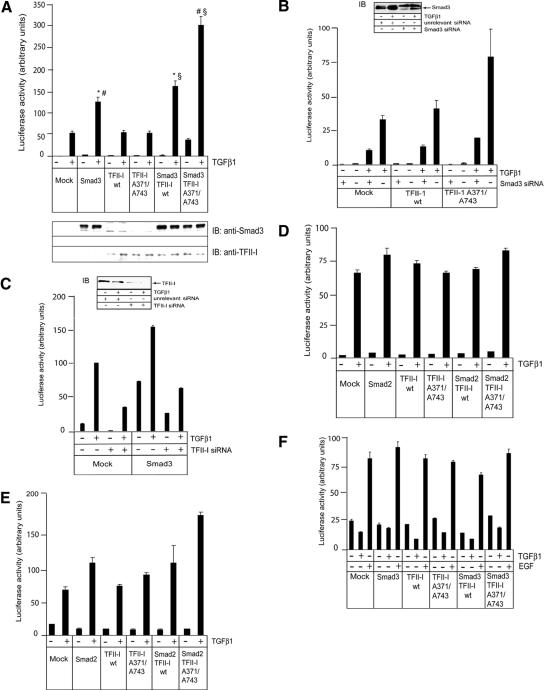
Abrogation of TFII-I Phosphorylation on Ser371 and Ser743 Increases TFII-I Cooperation with Smad3 in Transcriptional Activation
To explore further the importance of TFII-I phosphorylation for transcriptional responses to TGFβ1, we performed a luciferase reporter assay with the TGFβ-responsive CAGA(12)-luc reporter. This reporter contains a minimal promoter and multiple CAGA boxes (Dennler et al., 1998). The minimal promoter contains the initiator (Inr) sequence of the adenovirus major late promoter, which is a binding site for TFII-I; the CAGA sequence is a specific binding site for Smad3 and Smad4 (Roy et al., 1997; Dennler et al., 1998; Roy, 2001). Because Smad2 requires another protein to mediate binding to a promoter DNA, use of the CAGA-containing reporter provided a possibility to correlate transcriptional activity with direct binding to DNA of activated Smad3. Thus, we explored whether TFII-I influenced Smad3-dependent activation of CAGA(12)-luc reporter. We used COS7 cells because they express TFII-I at a lower level than other cells, and therefore have a low background when mutated TFII-I is analyzed in transfection experiments (Casteel et al., 2002). We observed that wild-type TFII-I cooperated with Smad3 in activation of the CAGA(12)-luc reporter (Figure 7A). Transfection of TFII-I alone did not affect the activation of CAGA(12)-luc reporter. The abrogation of TGFβ1-dependent phosphorylation of TFII-I resulted in a further increase of cooperation, as shown by the transfection of the Ser371,743Ala mutated TFII-I with Smad3; the mutated TFII-I consistently increased Smad3-dependent induction of the reporter 2.0 fold, whereas the wild-type TFII-I increased Smad3-dependent transcription 1.3-fold, compared with TGFβ1-treated cells transfected with Smad3 only. Our results suggest that the phosphorylation at serine residues 371 and 743 may inhibit the cooperation between Smad3 and TFII-I in regulation of transcription.
Figure 7.
Abrogation of TGFβ1-dependent phosphorylation of TFII-I at Ser371 and Ser743 increased TFII-I-dependent cooperation with Smad3 in transcriptional regulation. (A) CAGA(12)-luc luciferase assay was performed using COS7 cells. Cells were transfected with myc-Smad3 (Smad3) and TFII-I wild-type (TFII-I wt) and mutant (TFII-I A341/A743) constructs, as indicated. Cells were treated with TGFβ1 (5 ng/ml), as indicated, and luciferase activity was measured after 18 h. Expression of Smad3 and TFII-I proteins was evaluated by immunoblotting of total cell extracts used for luciferase assay. Antibodies specific to Smad3 and TFII-I were used, as indicated. A representative experiment out of three performed, is shown. *p < 0.05, cells transfected with Smad3 and TFII-I wild-type, compared with Smad3 transfected cells. #p < 0.001, cells transfected with Smad3 and mutant TFII-I, compared with Smad3 transfected cells. §p < 0.005, cells transfected with Smad3 and TFII-I wild-type, compared with cells transfected with Smad3 and mutant TFII-I. (B) Smad3 siRNA strongly inhibited activation of CAGA(12)-luc reporter. COS7 cells were transfected with Smad3-specific siRNA, nonspecific siRNA, wild-type or mutant TFII-I, and treated with TGFβ1 (5 ng/ml), as indicated. Inserts shows down-regulation of Smad3 expression by siRNA. (C) Endogenous TFII-I is required for Smad3-dependent activation of CAGA(12)-luc reporter. COS7 cells were transfected with TFII-I specific siRNA, nonspecific siRNA, Smad3, and treated with TGFβ1 (5 ng/ml), as indicated. Inset shows down-regulation of endogenous TFII-I by siRNA. (D) Smad2 and TFII-I do not affect TGFβ-dependent induction of CAGA(12)-luc reporter. 293T cells were transfected, as described in A, except Smad2 was transfected instead of Smad3. Cells were treated and luciferase activity was measured, as described in A. (E) Ser341,743Ala mutant of TFII-I cooperated with Smad2 in activation ARE-luc luciferase reporter. 293T cells were transfected with Smad2, wild-type and mutant TFII-I, and treated with TGFβ1 (5 ng/ml), as indicated. Luciferase activity was measured, as described in A. (F) TFII-I and TGFβ did not affect activation of SRE-luc reporter. 293T cells were transfected with Smad3, wild-type and mutant TFII-I, and treated with TGFβ1 (5 ng/ml) and EGF (1 ng/ml), as indicated. Luciferase activity in all assays (A–F) was measured as described in A. Transfection efficiency in all luciferase reporter assays (A–F) was normalized to β-galactosidase activity of cotransfected LacZ plasmid. Representative experiments out of three performed (A–F), are shown.
To explore role of endogenous Smad3 and TFII-I in activation of CAGA(12)-luc reporter, we used small interfering RNA (siRNA) specific to Smad3 and TFII-I (Figure 7, B and C, insets). We found that inhibition of Smad3 expression strongly blocked activation of the reporter (Figure 7B). Transfection of wild-type or mutant TFII-I did not affect luciferase activity. Because activation of CAGA(12)-luc reporter is dependent on Smad3 binding to the CAGA elements in the promoter, experiment with Smad3 siRNA indicated that TFII-I, endogenous or transfected, cannot modulate reporter activity without Smad3. Interestingly, down-regulation of TFII-I with specific siRNA decreased TGFβ- and Smad3-dependent induction of CAGA(12)-luc reporter (Figure 7C). This suggests that endogenous TFII-I is required for efficient Smad3-dependent activation of the reporter. In contrast to Smad3, Smad2 does not bind to DNA directly and does not interact with CAGA elements. As expected, expression of Smad2 with wild-type or mutant TFII-I did not affected TGFβ-dependent induction of CAGA(12)-luc reporter (Figure 7D). However, when we tested Smad2-responsive ARE-luc reporter, Ser371,743Ala mutant of TFII-I cooperated with Smad2 (Figure 7E). Smad2 binds to the ARE promoter via FAST protein, and expression of both proteins may affect responsiveness of ARE-luc reporter, compared with Smad3-dependent CAGA(12)-luc. Experiments with Smad-independent SRE-luc reporter confirmed that TFII-I does not affect transcriptional regulation in a nonspecific way (Figure 7F). Notably, transfection of TFII-I had a marginal effect on activation of SRE-luc reporter by epidermal growth factor (Figure 7F). Thus, reporter assays showed that TFII-I cooperates with Smad3 via forming a complex with Smad3 and not via a Smad-independent mechanism.
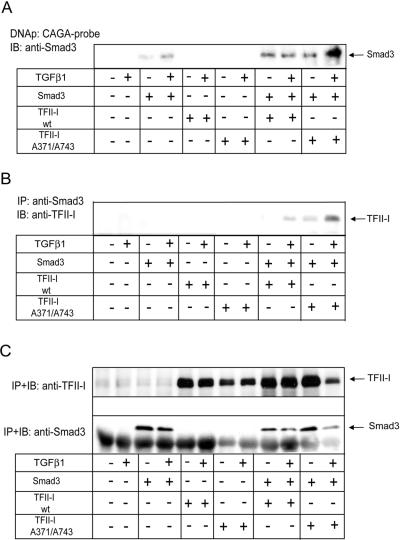
To explore whether TFII-I affects binding of Smad3 to CAGA elements, we performed a DNA precipitation assay (Figure 8A). We observed a strong binding of Smad3 to the CAGA-probe upon expression of the wild-type and Ser371,743Ala mutant TFII-I. For cells transfected with the Ser371,743Ala mutant TFII-I, Smad3 binding was further enhanced upon treatment of cells with TGFβ1 (Figure 8A). TGFβ1 had a marginal effect on Smad3 binding upon expression of wild-type TFII-I. This suggests that direct binding to the CAGA elements is not sufficient for the maximal Smad3-dependent transcriptional activation, and other ligand-induced events are required, e.g., phosphorylation of Smad3 and interaction with other proteins. Smad3 transfected alone showed weak binding to the CAGA probe. This binding was enhanced upon treatment with TGFβ1. Because TFII-I did not affect the stability of Smad3, our results suggest that TFII-I enhanced binding of Smad3 to the CAGA box, and abrogation of TGFβ1-dependent phosphorylation of TFII-I enhanced further Smad3 binding.
Figure 8.
TFII-I transfection increased binding of Smad3 to the CAGA elements. (A) DNA precipitation assay with immobilized CAGA-probe showed increased binding of myc-Smad3 (Smad3) to the probe upon cotransfection of myc-TFII-I Ser371,743Ala mutant (TFII-I A371/A743) and treatment with TGFβ1, compared with binding of myc-Smad3 cotransfected with wild-type myc-TFII-I (TFII-I wt). COS7 cells were transfected with myc-Smad3 and TFII-I plasmids, and treated with TGFβ1 (5 ng/ml), as indicated. Proteins bound to CAGA probe were separated by SDS-PAGE, and transferred onto nitrocellulose membrane. Smad3 was detected by immunoblotting with anti-Smad3 antibody. The migration position of Smad3 is shown by an arrow. (B) Smad3 and TFII-I form a complex. COS7 cells were transfected with myc-Smad3, myc-TFII-I wild-type and Ser371/743Ala mutant, and empty vector, as described in B, and were treated with TGFβ1 (5 ng/ml), as indicated. Proteins immunoprecipitated with anti-Smad3 antibodies were immunoblotted with anti-TFII-I antibodies. The anti-Smad3 and anti-TFII-I antibodies used recognize also endogenous proteins. Migration position of TFII-I is shown by an arrow. (C) Expression of Smad3 and TFII-I in cells which were used in DNA-precipitation and coimmunoprecipitation assays. Transfection of Smad3 and TFII-I plasmids was performed in identical manners for the two assays, and transfected cells were divided and used for assays at the same time. Expression of Smad3 and TFII-I proteins was evaluated by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting of Smad3 and TFII-I with respective specific antibodies which recognize epitopes also in endogenous proteins. Migration positions of Smad3 and TFII-I are shown by arrows. Representative experiments out of three (A–C) performed are shown.
To explore whether Smad3 and TFII-I could form a complex, we performed a coimmunoprecipitation assay of Smad3 cotransfected with wild-type or mutant myc-TFII-I. We observed Smad3 in a complex with wild-type TFII-I upon treatment of cells with TGFβ1 (Figure 8B). Mutant TFII-I formed a complex with Smad3 even in the absence of treatment with ligand. Ligand-independent complex formation between wild-type TFII-I and Smad3 was weak (our unpublished data), and the complex formation was enhanced after addition of TGFβ1 (Figure 8B). Whether interaction between TFII-I and Smad3 is direct, remains to be investigated. Because TFII-I cooperated with Smad3 in transcriptional regulation, a preservation of the complex may increase the transcriptional cooperation between TFII-I and Smad3, whereas TGFβ1-dependent phosphorylation of TFII-I at Ser371 and Ser743 may restrain this transcriptional cooperation.
Serine residues 371 and 743 are located in a sequence context suggesting that they can be phosphorylated by cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG). In agreement with this prediction, site-directed mutagenesis of both serine residues abrogated TFII-I phosphorylation by PKG (Casteel et al., 2002). Thus, we explored whether inhibition of PKG would block TGFβ1-dependent phosphorylation of TFII-I. To exclude an influence of basal phosphorylation of TFII-I, we performed two-dimensional phosphopeptide mapping of 32P-labeled TFII-I, because it allows evaluation of phosphorylation of specific peptides. We found that pretreatment of cells with the PKG-specific inhibitor K5823 decreased, but did not abolish, phosphorylation of TFII-I (Figure 9, A and B). Pretreatment of cells with the H7 inhibitor of broad specificity had stronger inhibitory effect (Figure 9C), but the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase inhibitor PD098059 did not affect the phosphorylation (our unpublished data). Thus, PKG may contribute to the TGFβ1-dependent phosphorylation of TFII-I, but an involvement of other kinase(s) is also possible. This suggests that the same residues, Ser371 and Ser743, may be phosphorylated by various kinases.
Figure 9.
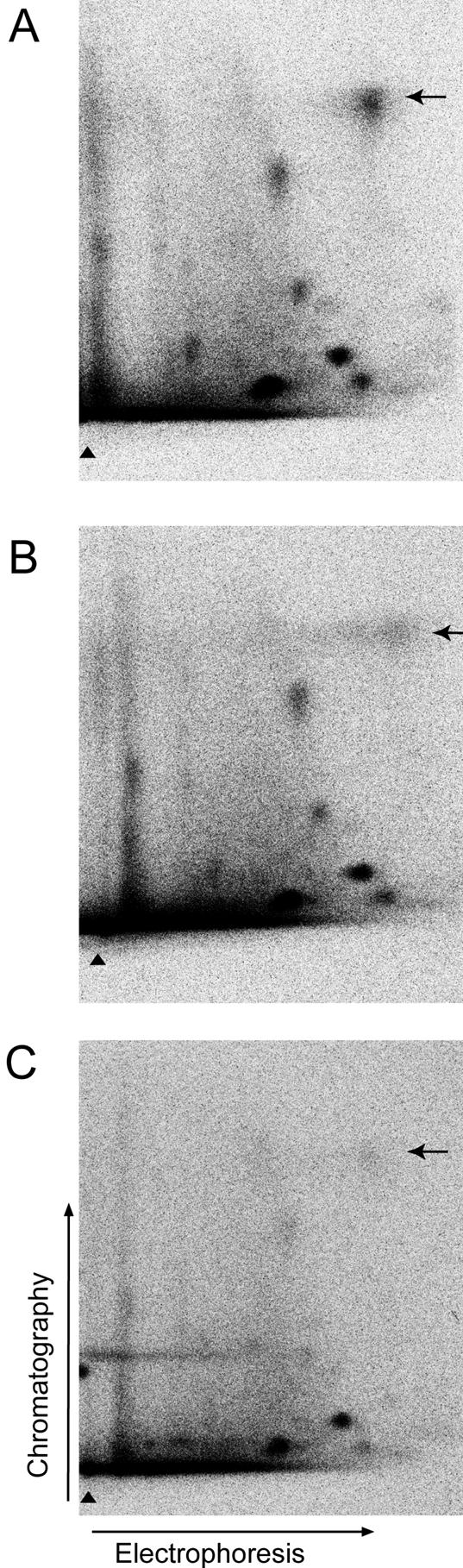
Inhibition of PKG decreases phosphorylation of TFII-I to moderate levels. COS7 cells were transfected with myc-Smad3, myc-TFII-I, and type I and type II TGFβ receptors plasmids. Cells were metabolically labeled with [32P]orthophosphate and were pretreated with TGFβ1 (10 ng/ml; A) and the inhibitors K5823 (1 μM; B) and H7 (10 μM; C). Phosphorylated TFII-I was immunoprecipitated from cells and subjected to two-dimensional phosphopeptide mapping. Phosphopeptide maps of TFII-I from cells not treated with inhibitors (A) and from cells treated with K5823 (B) and H7 (C) are shown. Migration position of peptides phosphorylated in TGFβ1-dependent manner is shown by arrows. Strongly phosphorylated peptide #1 is shown (compare with Figure 5E). Pictures from a representative experiment out of two performed are shown.
DISCUSSION
We performed a phosphoproteome profiling of TGFβ1 signaling in MCF-7 cells to unveil novel regulatory targets of TGFβ1. 2D-GE and peptide mass fingerprinting using MALDI TOF MS in combination with 32P metabolic labeling of cells provided reproducible generation of phosphoproteome maps and high efficiency of protein identification (Souchelnytskyi, 2002b; Figeys, 2003; Patterson and Aebersold, 2003). We identified 32 proteins that changed their phosphorylation upon TGFβ1 treatment of MCF-7 cells; 26 of these proteins are novel targets of TGFβ1 (Table 1, Figure 1, and Supplementary Figure A).
The most striking feature of the identified patterns of protein phosphorylation is their high dynamics, which complicates clustering of proteins according to the time dependence of phosphorylation (Supplemental Figure B). This is not a particularity of TGFβ signaling, because a highly dynamic protein phosphorylation was also observed in mouse fibroblasts stimulated with platelet-derived growth factor (Soskic et al., 1999).
The second conclusion is that an increased expression of Smad3 or Smad2 influenced TGFβ1-regulated phosphorylation of proteins. Five types of responses were identified, depending on which Smad protein had an effect on protein phosphorylation (Figure 2). Smad3 can bind DNA directly, whereas Smad2 does not. Interaction of these Smad proteins with activated TGFβ receptors can also be modulated in different ways (Derynck et al., 2001; Souchelnytskyi, 2002a; Wakefield and Roberts, 2002). Smad3 and Smad2 show different responses in a number of assays (Piek et al., 2001), and ablation of their respective genes in mice resulted in different phenotypes (Chang et al., 2002). Thus, Smad3 and Smad2 mediate different biological activities. Our data conforms to the notion that Smad3 and Smad2 have different signaling potential. Smad2 and Smad3 can bind different proteins, serving as docking molecules, or they could affect expression of phosphorylated proteins in different ways. However, the mechanism of the described Smad dependency of protein phosphorylation remains to be explored.
TGFβ1-dependent changes of protein phosphorylation showed examples of relatively high amplitude (Figure 2 and Supplemental Figure B), compared with the amplitudes of protein expression (Bratt et al., 2001; Kanamoto et al., 2002). Thirty proteins out of 32 identified showed changed levels of phosphorylation of >50% (Figure 2 and Supplemental Figure B), whereas most of the changes in protein expression was ∼30% (Bratt et al., 2001; Kanamoto et al., 2002). This confirms the high dynamics of protein phosphorylation induced by TGFβ1.
TGFβ, via phosphorylation and activation of Smad3 and Smad2, initiates signaling pathways that result in Smad-dependent regulation of gene transcription (Chang et al., 2002; Wakefield and Roberts, 2002; Shi and Massagué, 2003). We explored the importance of TGFβ1-dependent phosphorylation of TFII-I, which plays a particular role in linking the basal transcriptional machinery and specific transcription factors (Roy, 2001). TFII-I may be involved in Williams–Beuren syndrome and X-linked agammaglobulinaemia (Yang and Desiderio, 1997; Pérez Juardo et al., 1998; Novina et al., 1999). TFII-I binds to the initiator (Inr) element, E-box sites and sis-inducible element (SIE) (Grueneberg et al., 1997; Roy et al., 1997; Kim et al., 1998; Parker et al., 2001). TFII-I binding to the Inr element mediates activation of transcription from promoters lacking TATA box. Negative cooperation of TFII-I with c-Myc may involve binding of TFII-I to E-box elements (Roy et al., 1993), and activation of c-fos was dependent on TFII-I binding to SIE and SRE (Roy et al., 1997; Kim et al., 1998; Casteel et al., 2002). The observed TFII-I-dependent modulation of the effect of TGFβ1 on expression of E2F2, cyclin D2, and cyclin D3 genes (Figure 6), is in agreement with the lack of TATA box sequences in promoters of these genes, and the presence of TFII-I- and Smad3 (CAGA)-binding elements (Brooks et al., 1996; Sears et al., 1997).
TFII-I functions are regulated by phosphorylation. TFII-I is phosphorylated predominantly on serine residues, but threonine and tyrosine phosphorylation were also identified (Yang and Desiderio, 1997; Novina et al., 1998). TFII-I phosphorylation did not affect binding of TFII-I to Inr element, but tyrosine and serine phosphorylation was required for transcriptional activation (Novina et al., 1998, 1999; Egloff et al., 2001; Kim and Cochran, 2001; Casteel et al., 2002; Cheriyath et al., 2002). The list of identified phosphorylation sites in TFII-I includes Tyr248, Tyr357, Ser371, Tyr462, Ser633, Ser627, and Ser743. Jak2, Src, and Btk kinase stimulate phosphorylation of Tyr248, which leads to an increased activation of c-fos (Grueneberg et al., 1997; Yang and Desiderio, 1997; Egloff et al., 2001; Kim and Cochran, 2001; Cheriyath et al., 2002). TFII-I phosphorylation at Ser633 and Ser627 by the Erk MAP kinase (Kim and Cochran, 2000), and phosphorylation at Ser371 and Ser743 by PKG (Casteel et al., 2002) also enhance the activation of c-fos transcription. Thus, TFII-I is a convergence point for various regulators of transcriptional activation, and the activity of TFII-I is regulated by phosphorylation.
We identified Ser371 and Ser743 as sites of TGFβ1-dependent phosphorylation; two-dimensional phosphopeptide mapping of wild-type and Ser371,743Ala mutant of TFII-I showed unambiguously specific phosphorylation of these two serine residues (Figures 3, 4, 5 and Supplemental Figures D and E). This phosphorylation was observed in endogenous and transfected TFII-I, and in two types of cells, COS7 and MCF-7. We also found that TFII-I in the basal state is phosphorylated on at least 11 amino acid residues. In agreement with a previous report (Novina et al., 1998), phosphopeptides that were subjected to phosphoamino acid analysis showed presence of phosphoserine and phosphothreonine in TFII-I in the basal state of phosphorylation (our unpublished data).
We found that a Ser371,743Ala mutant of TFII-I was a more potent coactivator of endogenous cyclin D2, cyclin D3, and E2F2 genes, and a Smad3-responsive reporter, compared with the wild-type TFII-I (Figures 6 and 7 and Supplemental Figures F and G). Reporter assays also showed that TFII-I required Smad3 for the cooperation in transcriptional activation and that TFII-I did not act on TGFβ/Smad3-responsive reporters on its own (Figure 7).
TGFβ1-dependent phosphorylation of TFII-I may have an effect on the expression of genes containing the initiator (Inr) element, but not on genes containing the TATA-box promoter, as was shown for Mullerian inhibiting substance gene (Morikawa et al., 2000). This provides a mechanism for adaptation of TGFβ-induced gene expression to physiological status of cells. Notably, availability and activity of TFII-I phosphorylating kinase may define which genes and to which level they will be regulated by TGFβ. It is known that mitogen-treated cells are less responsive to growth inhibitory action of TGFβ (Derynck et al., 2001; Souchelnytskyi, 2002a; Wakefield and Roberts, 2002). We observed cooperative effect of TFII-I on expression of genes involved in cell cycle progression, e.g., cyclin D2, cyclin D3, and E2F2 (Figure 6). Stimulation of these genes would counteract TGFβ growth inhibitory action. Thus, enhanced activity of TFII-I kinase, e.g., PKG, may result in a strong TGFβ-dependent phosphorylation of TFII-I. This may lead to attenuation of growth inhibitory activity of TGFβ, whereas other activities may not be affected. It would be important to explore whether such modulation of TGFβ signaling contributes to the dual role of TGFβ in tumor progression, when abrogation of growth inhibitory action of TGFβ and stimulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation are thought to be crucial for TGFβ-promoted metastasis (Derynck et al., 2001; Souchelnytskyi, 2002a; Wakefield and Roberts, 2002).
Increased binding of Smad3 to the CAGA-element upon coexpression with the TFII-I Ser371,743Ala mutant (Figure 8B), compared with a coexpression of Smad3 with wild-type TFII-I, may provide an explanation for the stronger costimulation of CAGA(12)-luc reporter by the mutant TFII-I (Figure 7). TFII-I cooperated with TGFβ1 in transcriptional regulation of cyclin D2, cyclin D3, and E2F2 genes, and abrogation of the TGFβ1-dependent phosphorylation of TFII-I at serine residues 371 and 743 led to a higher transcriptional activity, compared with the wild-type phosphorylatable TFII-I (Figure 6). Thus, TGFβ1-induced phosphorylation of TFII-I may be an example of a feedback mechanism on the level of transcriptional regulation of a set of genes. This mechanism may include TGFβ-dependent stimulation of transcription via activation of Smad3 and simultaneous restrain of transcriptional activation via phosphorylation of TFII-I. Combination of such mechanisms may contribute to selective and fine-tuned activation of genes by TGFβ.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Pilz for TFII-I constructs. This work was supported in part by grants from the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, the INSERM/VR, the EU-program T-ANGIOVASC, the Swedish Cancer Society, the Swedish Research Council, the Hiroshima University, and Merck KGaA (to S. S.).
This article was published online ahead of print in MBC in Press (http://www.molbiolcell.org/cgi/doi/10.1091/mbc.E05-03-0257) on July 29, 2005.
The online version of this article contains supplemental material at MBC Online (http://www.molbiolcell.org).
References
- Bratt, C., Lindberg, C., and Marko-Varga, G. (2001). Restricted access chromatographic sample preparation of low mass proteins expressed in human fibroblast cells for proteomic analysis. J. Chromatogr. A. 909, 279-288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, A. R., Shiffman, D., Chan, C. S., Brooks, E. E., and Milner, P. G. (1996). Functional analysis of the human cyclin D2 and cyclin D3 promoters. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 9090-9099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteel, D. E., Zhuang, S., Gudi, T., Tang, J., Vuica, M., Desiderio, S., and Pilz R. B. (2002). cGMP-dependent protein kinase Iβ physically and functionally interacts with the transcription regulator TFII-I. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 32003-32014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H., Brown, C. W., and Matzuk, M. M. (2002). Genetic analysis of the mammalian transforming growth factor-beta superfamily. Endocr. Rev. 23, 787-823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheriyath, V., and Roy, A. L. (2000). Alternatively spliced isoforms of TFII-I: complex formation, nuclear translocation and differential gene regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 26300-26308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheriyath, V., Desgranges, Z. P., and Roy, A. L. (2002). c-Src-dependent transcriptional activation of TFII-I. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 22798-22805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennler, S., Itoh, S., Vivien, D., ten Dijke, P., Huet, S., and Gauthier, M. (1998). Direct binding of Smad3 and Smad4 to critical TGFβ-inducible elements in the promoter of human plasminogen activator inhibitor-type 1 gene. EMBO J. 17, 3019-3100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck, R., Akhurst, R. J., and Balmain, A. (2001). TGF-beta signalling in tumor suppression and cancer progression. Nat. Genet. 29, 117-129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egloff, A. M., and Desiderio, S. (2001). Identification of phosphorylation sites for Bruton's tyrosine kinase within the transcriptional regulator BAP/TFII-I. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 27806-27815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanayan, S., Firth, S. M., Butt, A. J., and Baxter, R. C. (2000). Growth inhibition by insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 in T47D breast cancer cells requires transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) and the type II TGF-beta receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 39146-39151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figeys, D. (2003). Proteomics in 2002, A year of technical development and wide-ranging applications. Anal. Chem. 75, 2891-2905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gobom, J., Nordhoff, E., Mirgorodskaya, E., Ekman, R., and Roepstorff, P. (1999). Sample purification and preparation technique based on nano-scale reversed-phase columns for the sensitive analysis of complex peptide mixtures by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 34, 105-116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grueneberg, D. A., Henry, R. W., Brauer, A., Novina, C. D., Cheriyath, V., Roy, A. L., and Gilman, M. (1997). A multifunctional DNA-binding protein that promotes the formation of serum response factor/homeodomain complex: identity to TFII-I. Gen. Dev. 11, 2482-2493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman, U. (2000). Sample preparation by SDS/PAGE and in-gel digestions. In: ed. P. Jollès and H. Jörnvall, Proteomics in Functional Genomics. Protein Structure Analysis. Basel, Switzerland: Birkhauser Verlag AG, 43-54
- Kanamoto, T., Hellman, U., Heldin, C.-H., and Souchelnytskyi, S. (2002). Functional proteomics of transforming growth factor-β1-stimulated Mv1Lu epithelial cells: Rad51 as a target of TGFβ1-dependent regulation of DNA repair. EMBO J. 21, 1219-1230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.-W., Cheriyath, V., Roy, A., and Cochran, B. H. (1998). TFII-I enhances activation of the c-fos promoter through interaction with upstream element. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 3310-3320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.-W., and Cochran, B. H. (2000). Extracellular signal-regulated kinase binds to TFII-I and regulates its activation of the c-fos promoter. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 1140-1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.-W., and Cochran, B. H. (2001). Jak2 activates TFII-I and regulates its interaction with extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 3387-3397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurisaki, K., Kurisaki, A., Valcourt, U., Terentiev, A., Pardali, K., ten Dijke, P., Heldin, C.-H., Ericsson, J., and Moustakas, A. (2003). Nuclear factor YY1 inhibits transforming growth factor-beta and bone morphogenetic protein-induced cell differentiation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23, 4494-4510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomnytska, M., Lukiyanchuk, V., Hellman, U., and Souchelnytskyi, S. (2004). TGFβ1-regulated proteins in human endothelial cells identified by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Proteomics 4, 995-1006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novina, C. D., Cheriyath, V., and Roy, A. (1998). Regulation of TFII-I activity by phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 33443-33448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novina, C. D., Kumar, S., Bajpai, U., Cheriyath, V., Zhang, K., Pillai, S., Wortis, H. H., and Roy, A. L. (1999). Regulation of nuclear localization and transcriptional activity of TFII-I by Bruton's tyrosine kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 5014-5024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning, G., Whyte, D. B., Martinez, R., Hunter, T., and Sudarsanam, S. (2002). The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science 298, 912-1934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa, N., Clarke, T. R., Novina, C. D., Watanabe, K., Haqq, C., Weiss, M., Roy, A., and Donahoe, P. K. (2000). Human Mullerian-inhibiting substance promoter contains a functional TFII-I-binding initiator. Biol. Reprod. 63, 1075-1083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder, K. (2000). Role of Ras and MAPKs in TGFβ signaling. Cytokinine Growth Factor Rev. 11, 23-35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker, R., Phan, T., Baumeister, P., Roy, B., Cheriyath, V., Roy, A., and Lee, A. S. (2001). Identification of TFII-I as the endoplasmic reticulum stress response element binding factor ERSF: its autoregulation by stress and interaction with ATF6. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 3220-3233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, S. D., and Aebersold, R. H. (2003). Proteomics: the first decade and beyond. Nat. Genet. 33, 311-323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez Jurado, L. A., Wang, Y.-K., Peoples, R., Coloma, A., Cruces, J., and Francke, U. (1998). A duplicated gene in the breakpoint regions of the 7q11.23 Williams-Beuren syndrome deletion encodes the initiator binding protein TFII-I and BAP-135, a phosphorylation target of BTK. Hum. Mol. Genet. 7, 325-334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piek, E., Ju, W. J., Heyer, J., Escalante-Alcade, D., Stewart, C. L., Weinstein, M., Deng, C., Kucherlapati, R., Bottinger, E. P., and Roberts, A. (2001). Functional characterization of transforming growth factor beta signaling in Smad2- and Smad3-deficient fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 19945-19953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy, A. L. (2001). Biochemistry and biology of the inducible multifunctional transcription factor TFII-I. Gene 274, 1-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy, A. L., Carruthers, C., Gutjahr, T., and Roeder, R. G. (1993). Direct role for Myc in transcription initiation mediated by interaction with TFII-I. Nature 365, 359-361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy, A., Du, H., Gregor, P. D., Novina, C. D., Martinez, E., and Roeder, R. G. (1997). Cloning of an Inr-and E box-binding protein, TFII-I, that interacts physically and functionally with USF1. EMBO J. 23, 7091-7104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears, R., Ohtani, K., and Nevins, J. R. (1997). Identification of positively and negatively acting elements regulating expression of the E2F2 gene in response to cell growth signals. Mol. Cell. Biol. 17, 5227-5235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevchenko, A., Wilm, M., Vorm, O., and Mann, M. (1996). Mass spectrometric sequencing of proteins from silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Chem. 68, 850-858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y., and Massagué, J. (2003). Mechanisms of TGF-β signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell 113, 685-700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soskic, V., Gorlach, M., Poznanovic, S., Boehmer, F., and Godovac-Zimmermann, J. (1999). Functional proteomics analysis of signal transduction pathways of the PDGF β receptors. Biochemistry 38, 1757-1764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souchelnytskyi, S. (2002a). Transforming growth factor-β signaling and its role in cancer. Exp. Oncol. 24, 3-12. [Google Scholar]
- Souchelnytskyi, S. (2002b). Proteomics in studies of signal transduction in epithelial cells. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 7, 359-371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield, L., and Roberts, A. (2002). TGF-β signaling: positive and negative effects on tumorigenesis. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 12, 22-29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakymovych, I., ten Dijke, P., Heldin, C.-H., and Souchelnytskyi, S. (2001). Regulation of Smad signaling by protein kinase C. FASEB J. 15, 553-555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W., and Desiderio, S. (1997). BAP-135, a target for Bruton's tyrosine kinase in response to B cell receptor engagement. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 9, 604-609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.