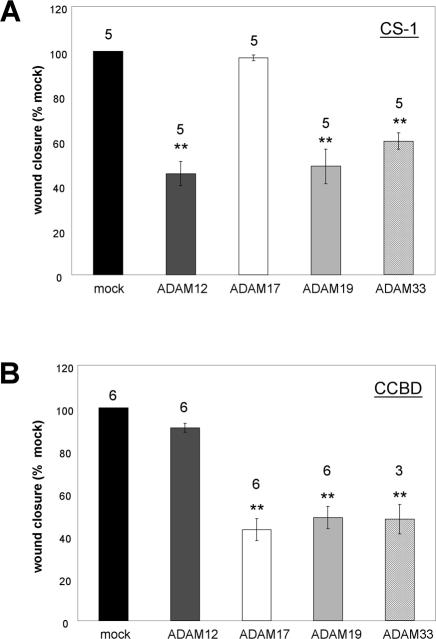
Figure 8.
Selective modulation of α4- or α5-mediated cell migration by ADAMs. (A) Scratch wound assays were performed as described previously. CHO-α4GFP cells transiently expressing ADAM12, ADAM17, ADAM19, or ADAM33 were compared for their relative ability to inhibit wound closure after 12 h on the CS-1 region of FN. 4 μg (per 6-cm dish) of cDNA encoding ADAM12, ADAM17, and ADAM19 were used for transfection. Because ADAM33 was consistently expressed at the cell surface at higher levels than the other ADAMs (Figure 6D), we used a 1:1 mixture of vector and ADAM33 cDNA (2 μg each) for the ADAM33-transfected samples to achieve comparable expression levels of all ADAMs tested. (B) Scratch wound assays were repeated as in panel A, except that α5-mediated cell migration was scored on the CCBD region of FN. For both A and B, the average wound closure plus or minus the SEM (error bars) from several independent experiments (numbers above the columns) is shown. ** indicates statistically significant difference compared with mock-transfected cells (p < 0.02 in Student's t test). A higher expression level (4 μg per 6-cm dish) of ADAM33 inhibited α5β1-mediated cell migration, but its effect on α4β1-mediated migration was diminished (Huang, Bridges, and White, unpublished data).