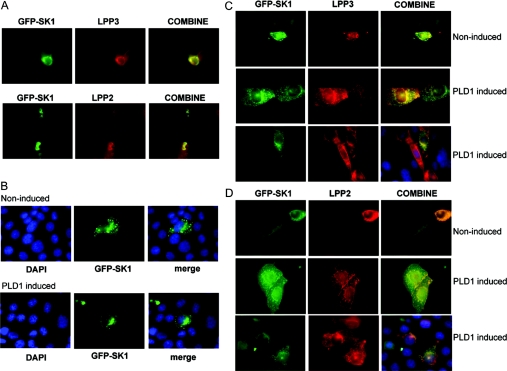
Figure 4. LPP–SK1 co-localization.
(A) HEK-293 cells stably expressing LPP3 or LPP2 were transiently transfected with plasmid construct encoding GFP-tagged SK1. LPP3 or LPP2 expression was detected using anti-LPP3 or anti-LPP2 antibodies respectively. The panel shows constitutive co-localization of LPP3 or LPP2 and SK1 (yellow fluorescence) in HEK-293 cells. (B–D) CHO cells were transiently transfected with vector or plasmid constructs encoding GFP-tagged SK1 (green) and FLAG-tagged LPP3 or FLAG-tagged LPP2 for 24 h prior to treatment without or with doxycycline to induce PLD1 expression. Epitope-tagged LPPs were visualized using anti-FLAG primary and TRITC-coupled secondary antibodies (red). (B) SK1 (green) moves to a perinuclear compartment under conditions of PLD1 induction. Cells were co-stained with DAPI (4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) to identify the nucleus. In this case, cells were not co-transfected with LPP plasmid constructs, but instead were co-transfected with corresponding empty vector. (C) In cells co-transfected with FLAG–LPP3 and GFP–SK1 plasmid constructs, LPP3 and SK1 are co-localized (yellow fluorescence) in control cells and move from a vesicular localization in the cytoplasm to a perinuclear compartment upon induction of PLD1. (D) In cells co-transfected with FLAG–LPP2 and GFP–SK1 plasmid constructs, LPP2 and SK1 are co-localized in cytoplasmic vesicles (yellow fluorescence), but fail to move to the perinuclear compartment upon induction of PLD1. In (C) and (D), additional panels are presented to show co-staining with DAPI (blue), GFP–SK1 and anti-FLAG antibody in PLD1-induced cells.