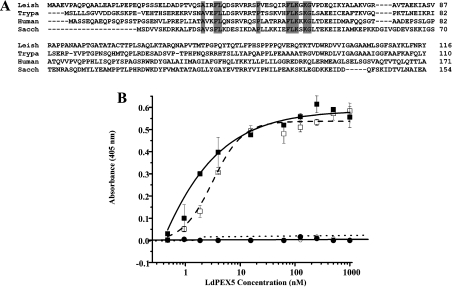
Figure 7. Mapping the LdPEX5 binding domain on LdPEX14.
(A) The multiple sequence alignment of the N-terminal region of the L. donovani (Leish), T. brucei (Trypa), human and S. cerevisiae (Sacch) PEX14 protein illustrates the conserved signature sequence (boldface). (B) Binding assay for the interaction of LdPEX5 with LdPEX14 N-terminal truncation mutants. Microtitre plates were coated with 1 μg/well wild-type LdPEX14 (□), ldpex14-(24–464) (■), ldpex14-(44–464) (○) or ldpex14-(64–464) (●), blocked with 2% milk powder in PBS 0.05% Tween 20 and incubated with various concentrations of LdPEX5 (0.4–860 nM). Amount of bound LdPEX5 was determined by indirect ELISA using anti-LdPEX5 rabbit antisera and goat anti-rabbit horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody.