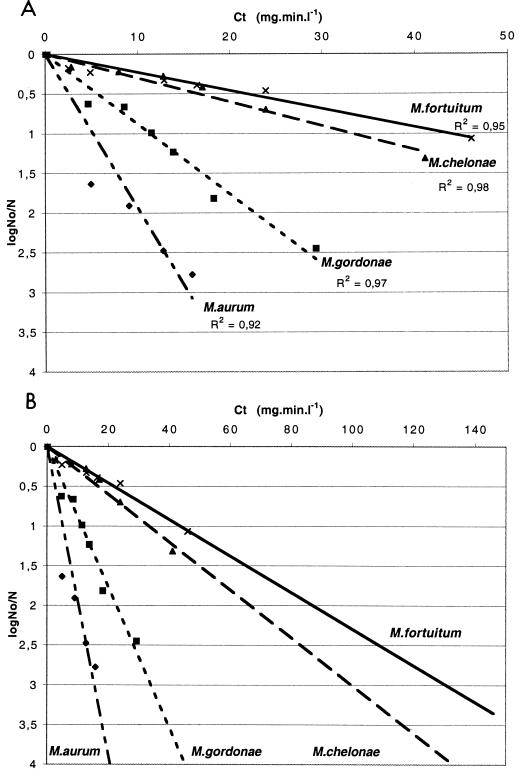
FIG. 2.
Inactivation of various mycobacterial species with chlorine. (A) The data presented are the averages of a minimum of two replicates. Linear regressions based on the logarithm of the fraction of the original number of mycobacteria remaining at time t (in minutes) for each strain were calculated as shown in Fig. 1 and used to calculate C · t values. For each species tested, the experimental conditions were pH 7, a temperature of 25°C, and an initial chlorine concentration of 0.5 mg/liter. Cells were grown in Middlebrook 7H9-Tween medium. No, initial number of CFU; N, number of CFU at the time of the assays. (B) Extrapolation of experimental curves to determine C · t values for 3 log units of cell death. Slopes were calculated as follows: M. aurum, y = 0.19 x; M. gordonae, y = 0.09 x; M. chelonae, y = 0.03 x; and M. fortuitum, y = 0.04 x. R2, correlation coefficient values.