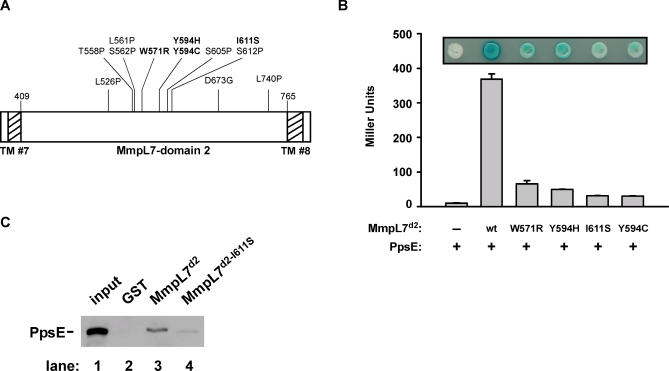
Figure 3. Identification of Residues in MmpL7 Domain 2 Required for PpsE Interaction.
(A) Twelve MmpL7 domain 2 mutants defective for PpsE binding were isolated in a reverse two-hybrid screen. These amino acid substitutions are displayed on a linear map of MmpL7 domain 2, with changes to amino acids other than proline or glycine in bold. Amino acid numbers correspond to positions in full-length MmpL7. TM domains 7 and 8 are denoted by hatched bars.
(B) Yeast strains expressing the PpsE prey construct and various MmpL7 domain 2 bait plasmids were transferred onto X-gal indicator plates (inset), and reporter activity was quantified from liquid cultures by monitoring β-galactosidase activity.
(C) Beads containing equal amounts of MmpL7 domain 2 and the I611S mutant were incubated with protein extracts containing myc-tagged PpsE and washed. Bound proteins were eluted and separated by SDS-PAGE, and PpsE was visualized by Western blot using anti-myc antibodies. GST-coated beads served as a negative control, and 1% of the protein extract added to the pulldown was loaded as a positive control (“input”).