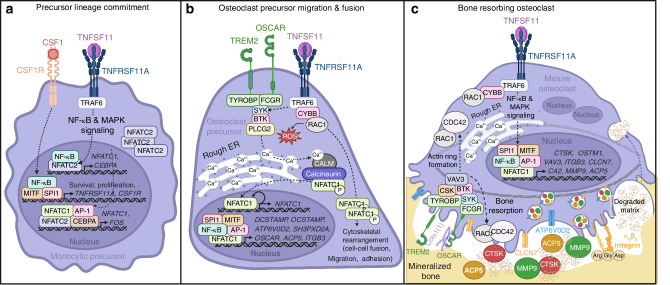
Fig. 2.
Signaling cascades during osteoclast differentiation. a CSF1 binds CSF1R on monocytic precursors activating transcription factors MITF and SPI1, promoting precursor survival and proliferation, and expression of TNFSF11 receptor (TNFRSF11A) and CSF1R. Surface expression of TNFRSF11A allows for TNFSF11 binding and activation of TRAF6 mediated NF-κB and MAPK signaling. Active NF-κB translocates to the nucleus where it promotes CEBPA expression and binds the NFATC1 promoter where it cooperates with NFATC2 to induce NFATC1 expression. CEBPA promotes expression of FOS which dimerizes with JUN to form active transcriptional complex AP-1. CEBPA and AP-1 in combination with NF-κB, NFATC2, and NFATC1 promote continued expression of FOS and NFATC1. b During TNFSF11-TNFRSF11A signaling, TRAF6 interacts with CYBB and RAC1 generating ROS and promoting cytoskeletal rearrangement necessary for precursor cell fusion, migration, and adhesion. TNFRSF11A signaling also mediates phosphorylation of adaptor proteins TYROBP and FCRG which activate downstream kinases, SYK, BTK, and PLCG2, triggering ER calcium release and activation of calmodulin (CALM)-dependent phosphatase calcineurin. Active calcineurin in turn dephosphorylates cytosolic NFATC1, allowing its translocation to the nucleus where it cooperates with transcription factors SPI1, MITF, AP-1, and NF-κB to promote osteoclast-specific gene expression. Additionally, NFATC1 binds its own promoter auto-amplifying its expression. c TNFRSF11A signaling continues to promote expression of proteins necessary for osteoclast resorption via NF-κB and MAPK signaling. αVβ3 integrin or TREM2/OSCAR can bind RGD sequences on ECM proteins in the bone matrix initiating the resorptive signaling cascade mediated by TYROBP, CSK, SYK, RAC1, and CDC42 to regulate actin ring formation and bone resorption. Endosomal trafficking mediates acidification of the sealing zone via transport of proton pump ATP6V0D2 and chloride channel CLCN7 and release of proteases such as CTSK, MMP9, and ACP5. Degraded bone matrix is removed via transcytosis and released into the local microenvironment. (Abbreviations: CSF1 colony stimulating factor 1, CSF1R CSF1 receptor, TNFRSF11A tumor necrosis factor receptor family member 11A, TNFSF11 tumor necrosis factor soluble factor 11, MITF melanocyte-inducing transcription factor, TRAF6 tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6, MAPK mitogen-activated protein kinase, NFATC1 nuclear factor of activated T cells 1, CEBPA CCAAT enhancer binding protein alpha, AP-1 activator protein 1, TREM2 triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2, OSCAR osteoclast-associated Ig-like receptor, TYROBP transmembrane immune signaling adaptor, FCRG Fc gamma receptor, SYK spleen associated tyrosine kinase, BTK Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, PLCG2 phospholipase C gamma 2, CALM calmodulin, CYBB cytochrome b-245 beta chain, ROS reactive oxygen species, DCSTAMP dendrocyte expressed seven transmembrane protein, OCSTAMP osteoclast stimulatory transmembrane protein, ATP6V0D2 ATPase H+ transporter V0 subunit d2, SH3PXD2A SH3 and PX domains 2A, ITGB3 integrin subunit beta 3, CLCN7 chloride voltage-gated channel 7, OSTM1 osteoclastogenesis associated transmembrane protein1, CTSK cathepsin K, ACP5 tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase 5, VAV3 vav guanine nucleotide exchange factor 3, CA2 carbonic anhydrase 2, MMP9 matrix metallopeptidase 9