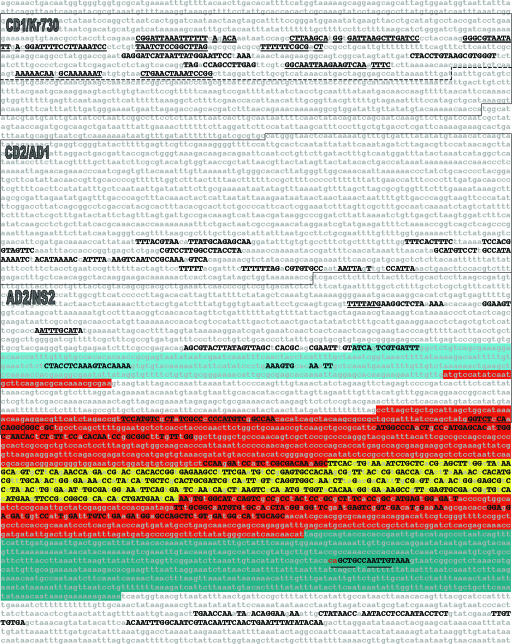
Fig. 2.
evoprinter analysis of the Drosophila Kr gene. The 7.7-kb (upper strand) of a 12-kb genomic EvoP that corresponds to the D. melanogaster reference DNA (nucleotides -4,207 to + 3,531) is shown. The EvoP was generated from blat readouts of the reference DNA aligned with D. simulans, D. yakuba, D. ananassae, D. pseudoobscura, and D. virilis DNAs. MCSs that are shared by all species are shown as uppercase black nucleotides. Boxed sequences represent the cis-regulatory regions described in Results and Discussion. Underlined MCSs within the CD1/Kr730 box contain known transcription-factor binding sites (35, 36). Underlined sequences in the AD2/NS2 box contain potential HB (TTTTAGT) and PDM1 (ATTTGCAT) DNA-binding sites, respectively. The D. melanogaster Kr transcribed sequence is annotated according to FlyBase as follows: 5′ untranslated leader (light blue), protein-encoding sequence (red; Zn finger domain, yellow), and the 3′ untranslated sequence (dark blue). Note that the protein-encoding sequence is interrupted by a 373-bp intron. The underlined nucleotides in the 3′ untranslated transcribed sequence correspond to E-box bHLH binding sites. evodif analysis of the individual test species revealed that the first two nucleotides of the first E-box (red letters) are shared by all tested species except for D. yakuba and D. ananassae.