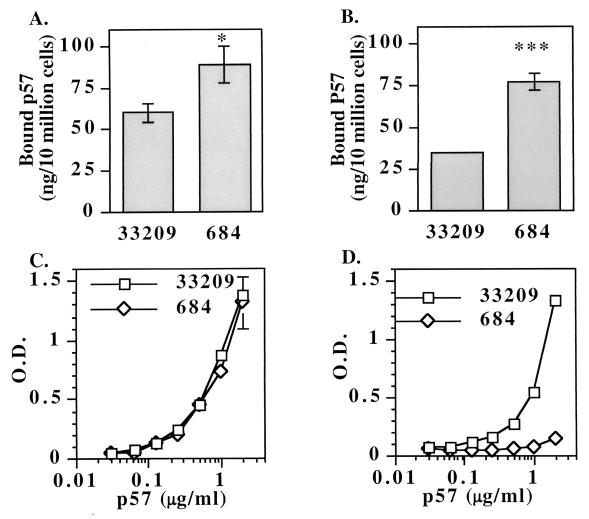
FIG. 6.
(A) p57 produced by R. salmoninarum strain 684 has 50% increased binding activity for chinook salmon anterior kidney leukocytes compared to the binding activity of an equivalent amount of p57 isolated from R. salmoninarum strain ATCC 33209. The data are averages ± standard errors of the means for binding of p57 to leukocytes from three salmon. The asterisk indicates that the results were significantly different at a P value of <0.05 (Student's t test). ECP was purified from culture supernatants of bacteria grown at the same time under identical conditions. The purification procedure and binding assay are described in Materials and Methods. (B) p57 from strain 684 exhibits a twofold increase in binding to rabbit red blood cells. The three asterisks indicate that the results were significantly different at a P value of <0.001 (Student's t test). (C) Identical amounts of immunoreactive p57 are present, as determined by a capture ELISA. MAb 3H1 was coated onto a plate, followed by dilutions of the ECP containing p57 from either strain ATCC 33209 or strain 684. Bacterial protein concentrations were determined by the Bradford protein assay. Biotinylated MAb 4D3 was used as a capture antibody, and this was followed by detection with a strepavadin-alkaline phosphatase conjugate. O.D., optical density. (D) Secreted p57 produced by strain 684 lacks the 4C11 epitope. The ELISA was identical to the ELISA whose results are shown in panel C, except that biotinylated MAb 4C11 was used instead of biotinylated MAb 4D3. The data are representative of the data from two experiments performed with the two preparations of ATCC 33209 and 684 ECP.