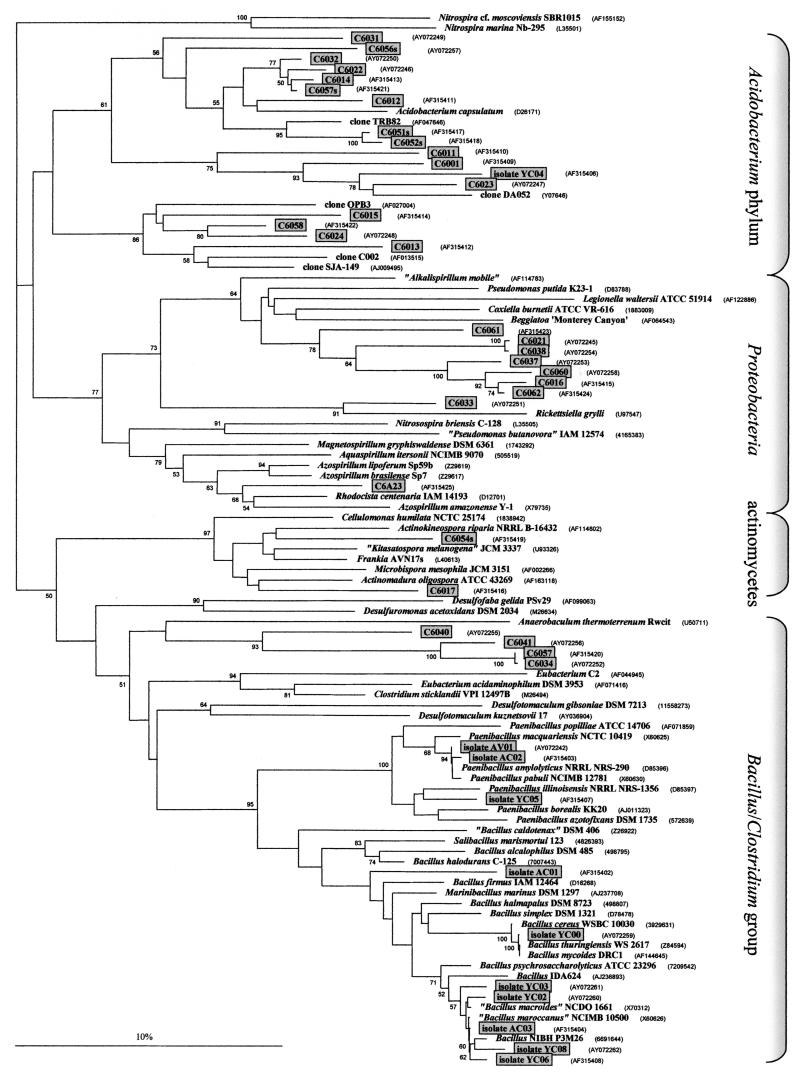
FIG. 2.
Phylogram of the 16S rRNA gene sequences. The sequences of two Nitrospira spp. served as an outgroup to root the phylogram. The clones that are framed and shaded were sequenced and deposited by us. The abbreviations used for the clones are explained in Materials and Methods. The alignment was done with 328 nt. The dendrogram was derived from 261 nt because of deletions and/or insertions in some sequences. The 59 GenBank sequences included in the phylogram were next most closely related to the clones obtained by us. These 59 were selected by employing the Ribosomal Database Project Phylip interface, followed by a BLASTN search. The scale bar indicates 10% nucleotide substitutions. Numbers at the branches indicate the percentages of the occurrence of the respective nodes in a bootstrap analysis of 1,000 resamplings. Only values above 50% are shown. Abbreviations (for all subsequent figures): A, cultured bacterium grown in Azospirillum medium; Y, cultured bacterium grown in YEM; C, amplification product of soil DNA or of a cultured bacterium from Chorbusch soil; V, amplification product of soil DNA or of a cultured bacterium from Villingen; F, amplification product from nifH; S, amplification product from nirS; K, amplification product from nirK; Z, amplification product from nosZ; 6, 16S rRNA; F, forward primer; R, reverse primer. The small letters behind the numbers are internal codes.