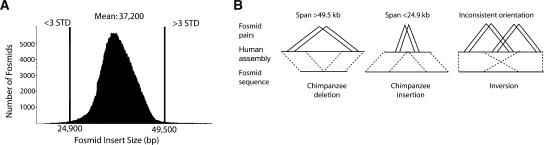
Figure 1.
Methodology. (A) Size distribution of 555,929 chimpanzee fosmids mapped unambiguously to the human genome assembly (build34). The distance between two end sequences was determined based on the coordinates within the human genome reference. A length threshold greater than or less than three SD beyond the mean (37.2 kb) was used to classify length discordancy. (B) A schematic depicting chimpanzee “deletions” (two or more fosmids showing a span >49.5 kb), “insertions” (two or more fosmids spanning <24.9 kb), and inversions in DNA (two or more fosmids with an inconsistent orientation of the end sequences with respect to the human genome for each breakpoint).