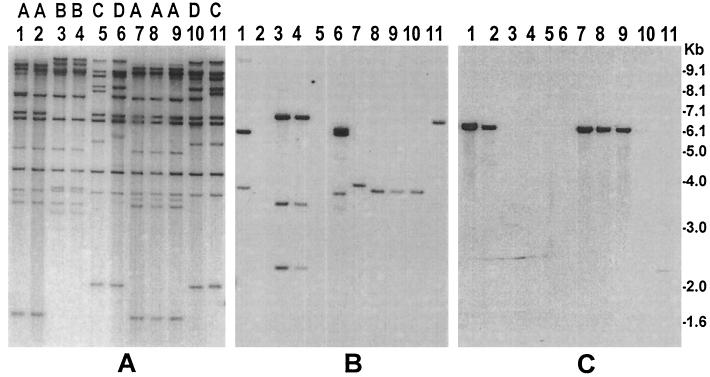
FIG. 2.
Molecular analysis of S. dysenteriae type 1 and S. flexneri strains isolated from environmental waters in Bangladesh and comparison with representative clinical Shigella strains. Genomic DNA was digested with HindIII, and corresponding Southern blots were hybridized with the rRNA gene probe (A), ipaBCD probe (B), and Shiga toxin gene probe (C). Ribotype designations A through D, which correspond to the rRNA gene restriction patterns of different strains, are shown on top of the corresponding lanes. Lanes 1, clinical S. dysenteriae type 1 strain (SD-16); lanes 2 and 7 through 9, S. dysenteriae type 1 strains (SD-477, SD-461, SD462, and SD-469) isolated from environmental waters; lanes 3 and 4, clinical S. dysenteriae type 2 strains (AF-8724 and AF-979); lanes 5, 10, and 11, S. flexneri strains (SF-525, SF-455, SF-526) isolated from environmental waters; lanes 6, clinical S. flexneri strain (SF-12163). Numbers indicating molecular sizes of bands correspond to the 1-kb DNA ladder (Gibco BRL) used as molecular size markers.