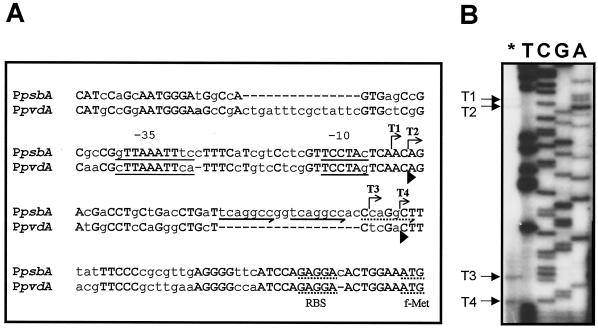
FIG. 2.
Structural analysis of the psbA promoter. (A) Alignment of the 158-nt region preceding the Pseudomonas strain B10 psbA start codon with the P. aeruginosa pvdA promoter. Identical nucleotides are capitalized and in boldface. The bent arrows indicate the minor (T1 and T2) and major (T3 and T4) transcription start sites of the psbA gene and the direction of transcription. The ISB and the TCCTA conserved motifs, which overlap the −35 and −10 regions, respectively, are underlined. The potential ribosome binding sites (RBS) and the transcriptional start codons (f-Met) of psbA and pvdA are underlined with dots. The locations of the conserved (solid arrows) and partially conserved (dotted arrow) direct repeats are indicated below the psbA sequence. Arrowheads below the pvdA sequence mark the positions of the 5′ ends of the pvdA T1 and T2 transcripts (9). (B) Localization of the transcriptional start sites of psbA. The asterisk indicates primer extension analysis of the psbA mRNA carried out with the 5′-end-labeled oligonucleotide PEpsbARV. Lanes T, C, G, and A represent sequencing ladders of pCAΔSh with the same oligonucleotide. These reactions were run in parallel with primer extension products to determine exactly the 5′ ends of the transcripts. The arrows on the left indicate the origins of psbA transcripts T1, T2, T3, and T4.