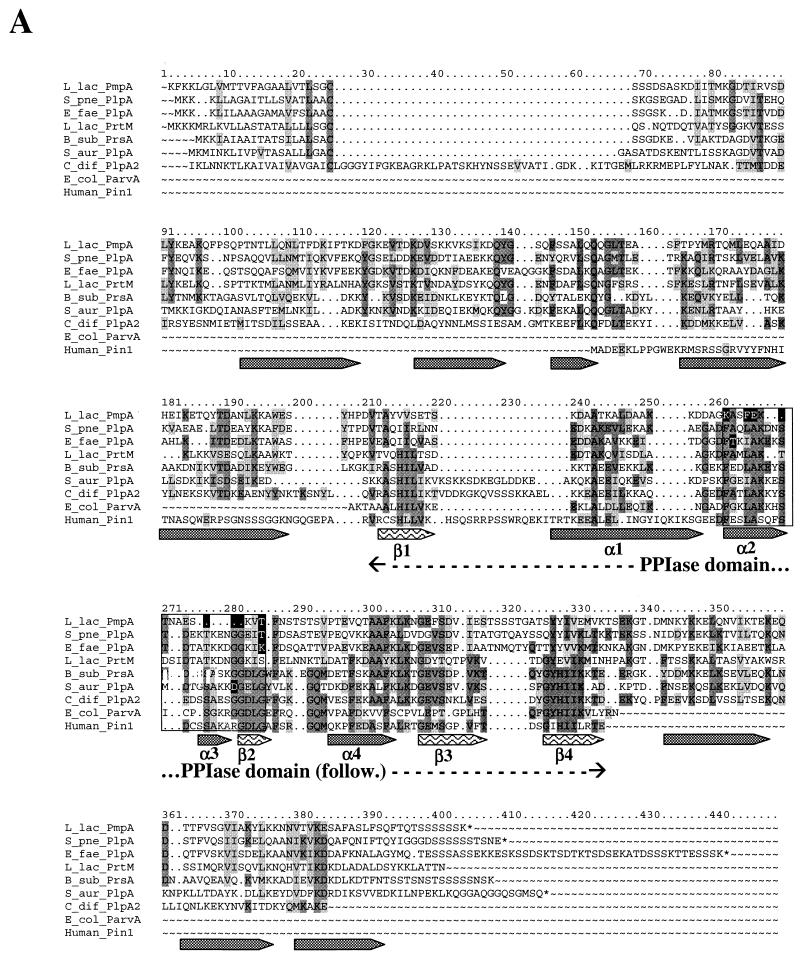
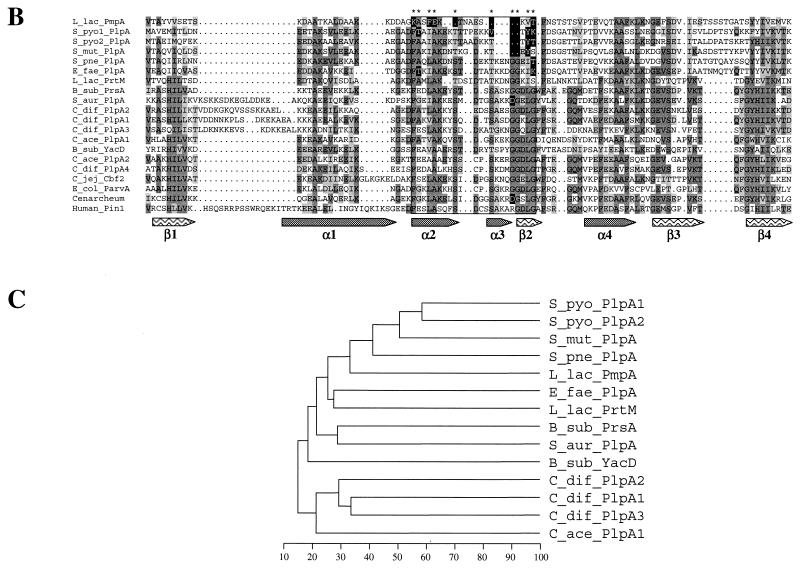
FIG. 2.
Multiple alignment of several PrsA-like proteins and PinA (A), more extensive alignment of PPIase domain of PLP with representative proteins belonging to the PPIase family (B), and phylogenetic dendrogram indicating the percentage of identity between the PLP of gram-positive bacteria (C). Protein sequences were aligned by using the PILEUP program (GCG). The alignments were edited manually and colored by Boxshade. Identical residues and conservative changes in more that half of the aligned sequences are on dark and light gray backgrounds, respectively. The boxed region contains the PPIase signature motif. Residues diverging from the PPIase signature are in white on a black background. The secondary structure of these proteins was predicted by the GORIV program (17). Alpha helix (gray arrows) and beta sheet (arrows with wave pattern) structures were indicated when predicted in more than 16 sequences at each position. The predicted structures fit with the known structure of the PPIase part of the human Pin1 protein is shown, for which the names of the domains are indicated under the arrows (α1 to α4 and β1 to β4) (6). The dendrogram was obtained by the successive use of the pileup, distances, and growtree programs of the GCG package. B_sub, B. subtilis; C_jej, C. jejuni; C_ace, C. acetobutylicum; C_dif, C. difficile; E_fae, E. faecalis; E_col, E. coli; L_lac, L. lactis; S_aur, S. aureus; S_mut, S. mutans; S_pne, S. pneumoniae; S_pyo, S. pyogenes.