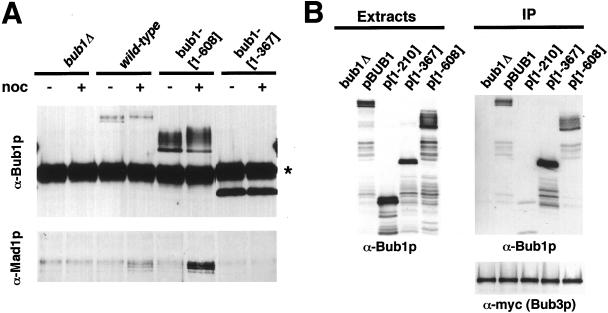
Figure 7.
Bub1-[1-608]p associates with Mad1p and Bub3p. (A) Coimmunoprecipitation of full-length Bub1p and bub1-[1-608]p with Mad1p. The strains shown, containing integrated Bub1 alleles expressed from the wild-type BUB1 promoter, were grown to log phase and were incubated with ± 15 μg/ml nocodazole for 2 h at 24°C. Immunoprecipitates were prepared using an α-Bub1p antibody, separated by SDS-PAGE, and transferred to nitrocellulose. The immunoblots were then probed with α-Bub1p and α-Mad1p rabbit antibodies as indicated. The strong band labeled (*) in the Bub1 blot is IgG heavy chain from the immunoprecipitation. Strains shown are YPH278, YFP2, YCD358, and YCD371. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of full-length Bub1p, bub1-[1-367]p, and bub1-[1-608]p with Bub3p. All strains contained a BUB3-myc allele in the genome. The experimental strains contained a wild-type BUB1 gene in addition to episomal MET25-promoted alleles as indicated. A bub1Δ strain served as control. Left: Bub1p Western blot using a rabbit α-Bub1p antibody. Right: Immunoprecipitation with an α-myc antibody recovered an equivalent amount of myc-tagged Bub3 protein (bottom). The immunoprecipitates were probed with rabbit α-Bub1p antibody (top). The strains were YKH300 (bub1Δ) or YKH238 with pBUB1, p[1-210], p[1-367], or p[1-608].