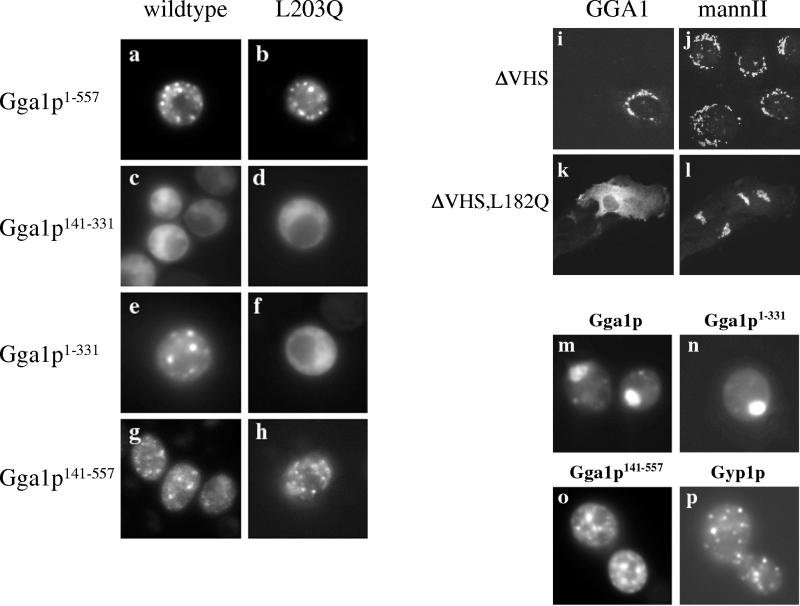
Figure 9.
Localization of truncated GFP-Gga1p. (a–h) Strains expressing wild-type or mutant versions of the indicated constructs were analyzed by GFP fluorescence. Punctate staining, characteristic of Golgi localization, was observed in a, b, e, g, and h. Cytosolic staining was observed in c, d, and f. (i–l) Localization of wild-type and mutant human GGA1ΔVHS. NRK cells were transiently transfected with pcDNA3-based vectors for expressing GGA1ΔVHS (residues 145–639, i–j) or mutant GGA1ΔVHS, L182Q (k and l). Cells were double-labeled for IIF with antibodies to GGA1 (R79709, i and k) and mannosidase II (j and l). GGA1ΔVHS localizes to the Golgi region, whereas GGA1ΔVHS, L182Q is cytosolic. (m–p) Localization of yeast Gga1p constructs in a class E mutant strain. The indicated constructs were expressed in a strain deleted of VPS27. Full-length GFP-Gga1p (m) and GFP-Gga1p1–331 (n) localize to the class E compartment. In contrast, GFP-Gga1p141–557 (o) localizes to distinct puncta throughout the cytoplasm in addition to limited staining near the vacuole. The early Golgi protein Gyp1p, expressed as an RFP fusion, localizes exclusively to Golgi puncta (p).