Figure 2.
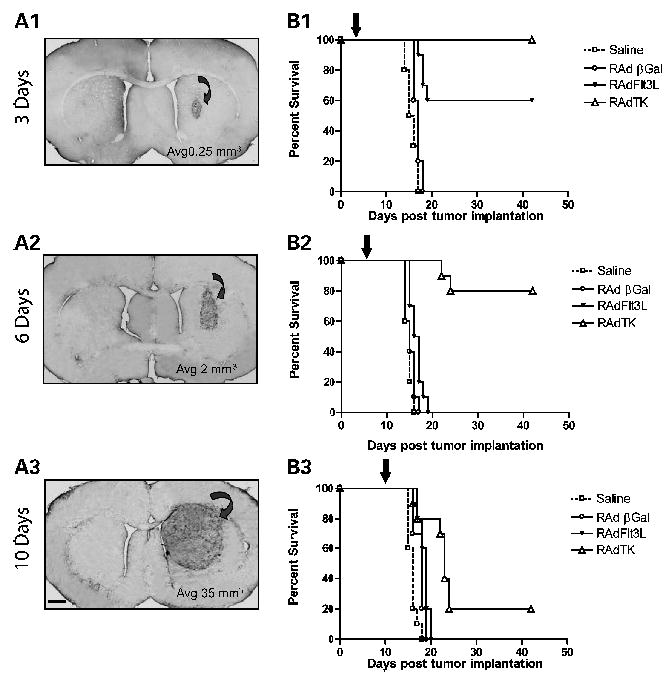
Single therapy with RAdTK improves survival in rats with microscopic brain tumors but is ineffective against large brain tumors. A, progressively increasing tumor sizes and volumes at 3 (A1), 6 (A2), and 10 (A3) days postimplantation of 5,000 CNS-1 cells into the brains of syngeneic Lewis rats. Tumor infiltration into the striatum was visualized using ED1, a marker of activated macrophages and microglial cells. Tumor volume was calculated to be 140 times greater at day 10 than at day 3. B, assessment of the survival efficiency of 8 × 107 plaque-forming units of either RAdTK (followed by 7 days of systemic GCV treatment) in rats bearing tumors of different sizes. Treatments were delivered to growing CNS-1 tumors either at 3 (B1), 6 (B2), or 10 (B3) days following tumor implantation (black arrow at the top of each of the graphs). Controls animals were injected with saline or RAdβgal. Notice the drop in effectiveness of RAdTK as it is injected into progressively larger tumors. Bar, for (A1) to (A3), shown in (A3), 150 μm.
