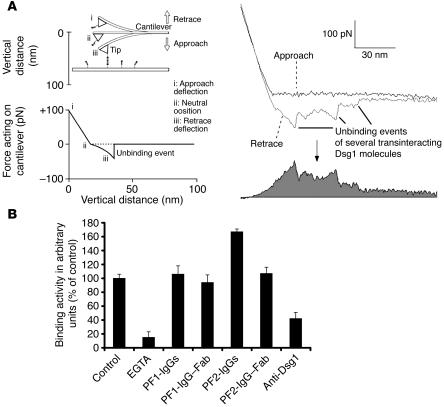
Figure 7.
Binding activity of Dsg1 in the presence or absence of PF-IgGs probed by AFM. (A) General working principle of force-distance cycles. Dsg1-Fc is covalently attached by PEG-linkers to the plate and cantilever tip of the AFM setup. Molecules are brought into contact by downward movement of the tip. During upward movement, a downward deflection of the cantilever will occur if plate- and tip-bound Dsg1 molecules undergo binding (left). Retrace and approach were subtracted, and the area below the resulting curve was integrated and taken as a measure for the average binding activity (right, gray). (B) Bar diagram shows binding activities of Dsg1 molecules in the presence or absence of antibodies. Binding activity was significantly reduced by incubation with EGTA (5 mM, 30 minutes) or the monoclonal antibody directed against Dsg1 (1:50). However, PF-IgGs (35 μg/ml, 30 min) did not reduce binding events in this cell-free system. Fab fragments from the PF-IgG fraction have been applied to rule out possible cross-linking effects of the PF-IgGs and were found not to reduce Dsg1-mediated binding (n = 4 for each condition).