Figure 1.
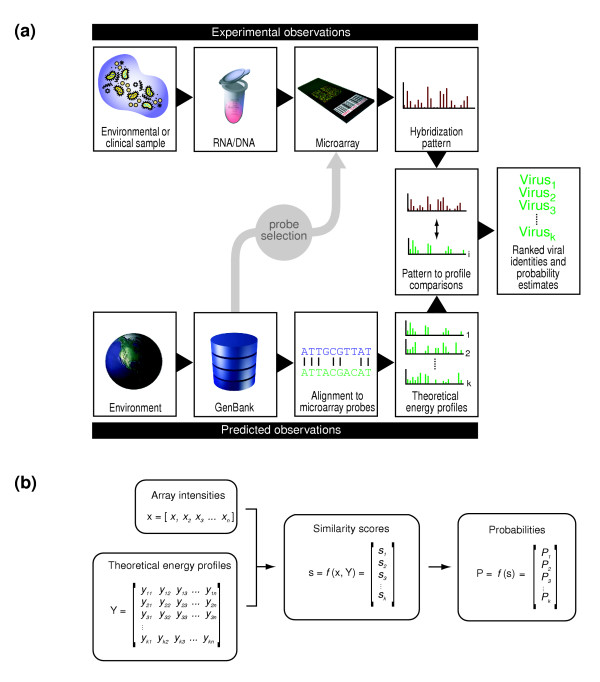
E-Predict algorithm. (a) Nucleic acid from an environmental or clinical sample is labeled and hybridized to a species detection microarray. The resulting hybridization pattern is compared with a set of theoretical hybridization energy profiles computed for every species of interest. Energy profiles attaining statistically significant comparison scores suggest the presence of the corresponding species in the sample. (b) Observed hybridization intensities are represented by a row vector x, where each intensity value corresponds to an oligonucleotide on the microarray. Theoretical hybridization energy profiles form a matrix of energy values, Y, where each row represents a profile, and each column corresponds to an oligonucleotide in x. A suitable similarity metric function compares x with each row of Y to produce a column vector of similarity scores, s. Statistical significance of the individual scores in s is estimated to produce the output column vector of probabilities, P, where each probability value corresponds to a profile in Y.
