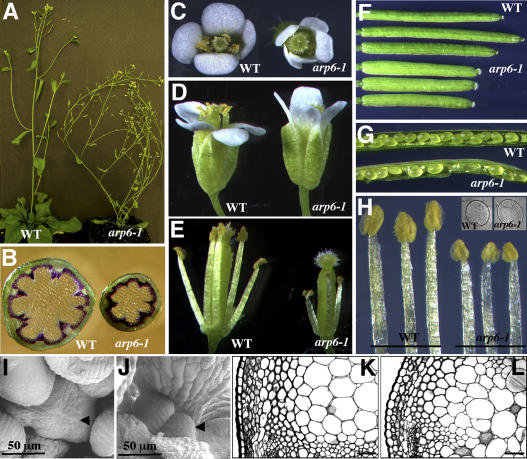
Figure 7.
Inflorescence and Flower Development in Long-Day-Grown arp6-1 Plants.
(A) Inflorescences of wild-type and arp6-1 plants.
(B) Cross sections of wild-type and arp6-1 inflorescence stems taken just below the first internode. Sections were stained for lignin with phloroglucinol.
(C) Top view of wild-type and arp6-1 flowers.
(D) Side view of wild-type and arp6-1 flowers.
(E) Side view of wild-type and arp6-1 flowers without sepals and petals.
(F) Fully expanded wild-type and arp6-1 siliques.
(G) Representative siliques of wild-type and arp6-1 plants opened to reveal developing seeds and unfertilized ovules in the arp6-1 fruit.
(H) Wild-type and arp6-1 stamens. Insets show pollen grains of each genotype.
(I) and (J) Scanning electron micrographs of wild-type (I) and arp6-1 (J) inflorescence meristems. Meristems are denoted by arrows.
(K) and (L) Toluidine blue–stained sections of wild-type (K) and arp6-1 (L) inflorescence stems shown at 40× magnification.