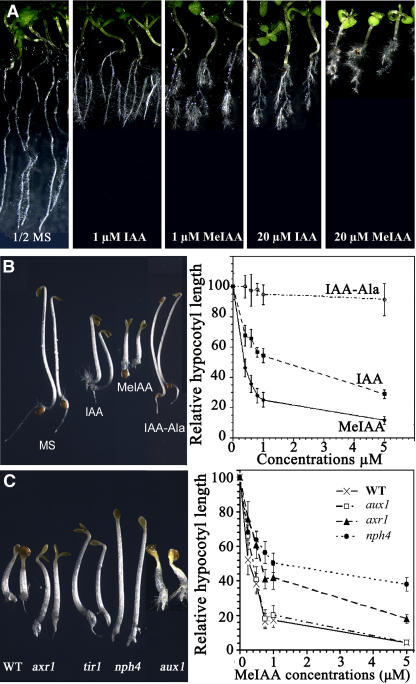
Figure 7.
Effects of Exogenous MeIAA on Arabidopsis Seedling Growth and Development.
(A) Comparison of Arabidopsis responses to exogenous MeIAA or IAA. Seeds of Columbia ecotype Arabidopsis were germinated in a Petri dish with solid half-strength (1/2) MS medium for 3 d after stratification for 3 d. The seedlings with average growth were transferred to half-strength MS medium with or without different concentrations of MeIAA or IAA and grown vertically for 5 d.
(B) Inhibition of hypocotyl elongation by MeIAA. Wild-type Arabidopsis seeds were germinated on medium containing various levels of the indicated chemicals for 3 d before hypocotyl length was measured. The seedlings at left were 3-d-old dark-grown wild-type Arabidopsis grown on half-strength MS medium or half-strength MS medium containing MeIAA or the indicated compounds. IAA, MeIAA, and IAA–Ala concentrations were 800 nM. Right, hypocotyl elongation of dark-grown seedlings is more inhibited by MeIAA than by IAA or IAA–Ala.
(C) Effect of MeIAA on the growth of the auxin-resistant mutants axr1, tir1, and nph4 and the auxin influx carrier mutant aux1. Seedlings were grown on 1 μM MeIAA in the dark for 3 d. The graph at right shows the decreased sensitivity of auxin-resistant mutants to MeIAA. Wild-type Arabidopsis and mutants were germinated on medium containing various concentrations of MeIAA for 3 d before hypocotyl length was measured. Because the phenotype of tir1 on MeIAA is very similar to that of axr1, only the axr1 data are shown. Error bars represent standard deviations.