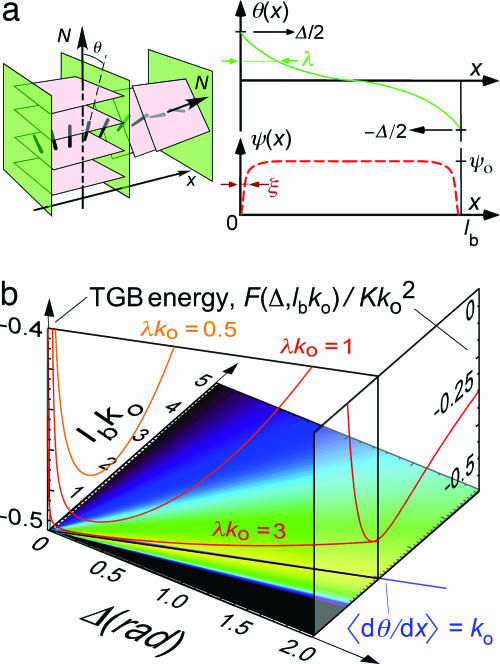
Fig. 1.
GBTGBA schematic structure and model energy. (a) GBTGBA structure in the limit that λ > ξ and plots showing the spatial variation of the smectic order parameter Ψ(x) and the director tilt θ(x) for one smectic block. The smectic blocks, of thickness lb, are separated by sharp MGBs shown in green. The molecular director, following a nearly uniform rate of twist, produces a total twist Δ across each smectic block, with essentially no twist in the MGBs. (b) Contour plot of F(Δ, αβ = lbko), the energy density of a GBTGBA relative to the SmA, as a function of lb and Δ. F(Δ, αβ) > 0 (colored black) and Δ(αβ)min, the local minimum of F(Δ, β) (colored yellow), follows a straight line corresponding to a mean twist equal to that preferred by the CN, i.e., with 〈dθ/dx〉 = Δ/lb = ko. Energy cross sections are plotted for Δ = 2.0 rad and Fm(Δ(αβ)) along the minimum energy trough, showing the latter to be very shallow and broad (note the energy scale difference), enabling wide variation in lb with little cost in energy.