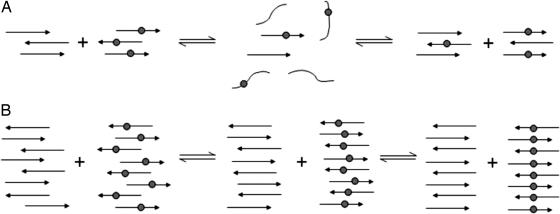
Fig. 8.
Schematic representations of the mixing of solutions of H1 and H1* at low (A) and high (B) concentrations. The labeled β-strands have a gray circle to represent the 13C-labeled residue 117. (A) Shown is the detachment of the β-strands from the domains of labeled and unlabeled peptide beginning a mixing of the strands. As the strands reattach in the aligned form, complete mixing occurs and the 13C labels are separated by an unlabeled residue 117, such that no coupling can occur despite the peptide being aligned with residue 117 in register across all strands. (B) Shown are the strands remaining within the domains of labeled and unlabeled peptide and beginning to slide over one another in a reptation mechanism until the entire peptide is aligned with residue 117 in register. The 13C-labeled carbonyls in the labeled domain of the peptide will then couple, resulting in a downshift of the 13C β-sheet band.