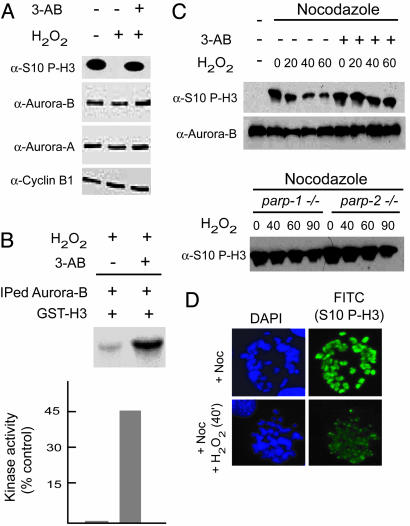
Fig. 2.
Functional relationship between Aurora-B and PARP-1 activation. (A) NIH 3T3 mouse fibroblasts were treated with H2O2 (1 mM) for the periods indicated in the presence or absence of the PARP-1 inhibitor 3-AB (cells were pretreated with 3 mM 3-AB for 3 h). (B) Kinase assay using immunoprecipitated Aurora-B from H2O2 (1 mM/60 min)-treated cells using GST-H3 as a substrate and [32P]-γATP. Pretreatment of cells with 3-AB (3 mM/3 h) increases in vitro Aurora-B kinase activity. Values were determined by densitometric analysis of the radioactivity (phospho-GST-H3) present in the substrate and are expressed as the percentage compared with a control sample (immunoprecipitated by using normal IgG). The lanes corresponding to + or - (3-AB) were taken from the same gel and sliced together as indicated. (C) Cells (Upper, NIH 3T3; Lower, MEFs from parp-1- and parp-2-null mice) were arrested in mitosis with nocodazole for 16 h and treated with 1 mM H2O2 as indicated in the presence of nocodazole. 3-AB (3 mM for 3 h) was added when necessary before H2O2 treatment. Western analysis was carried out by using antibodies directed against P-H3/Ser-10. The levels of Aurora-B were analyzed as a control. (D) NIH 3T3 cells were treated with nocodazole for 6-8 h and then with H2O2 for 40 min. Cells were harvested by mitotic shake-off, cytospun onto slides, and immunostained by using antibodies directed against P-H3/Ser-10. Cells untreated with H2O2 served as a control. DAPI was used as a counterstain.