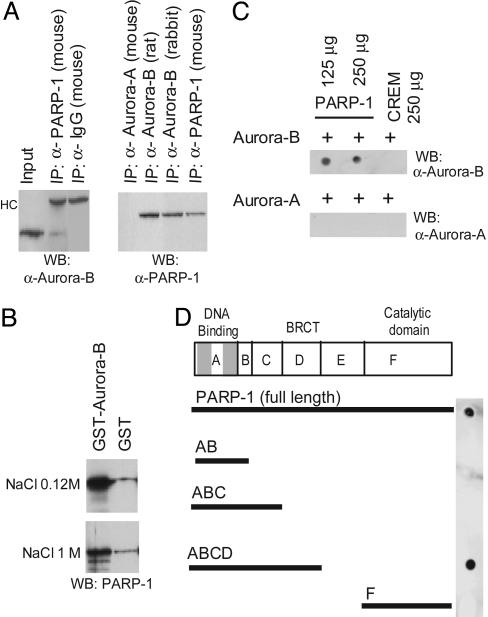
Fig. 3.
Aurora-B interacts specifically with PARP-1. (A) Extracts from GC-spg1 cells were immunoprecipitated with the indicated antibodies, and the immunocomplexes were probed with either anti-Aurora-B or anti-PARP-1 antibodies. Aurora-A does not interact with PARP-1. HC, heavy chain. (B) GST or GST-Aurora-B proteins coupled to glutathione beads were incubated with purified PARP-1 protein and washed with a low- or high-salt buffer. Western blotting with anti-PARP-1 antibodies was used to analyze the pulled-down products. (C) Far-Western analysis. Two aliquots of 125 μg and 250 μg of purified PARP-1 protein were spotted onto a nitrocellulose filter, hybridized with Aurora-A or Aurora-B, washed, and probed with anti-Aurora-A and/or anti-Aurora-B antibodies. (D) Equimolar aliquots of purified full-length PARP-1 and of truncated proteins corresponding to different functional domains were spotted onto a nitrocellulose filter, hybridized with Aurora-B, and revealed with anti-Aurora-B antibodies. The interaction between the kinase and PARP-1 involves the BRCT domain (amino acids 373-524), whereas no binding occurs between Aurora-B and the PARP-1 catalytic domain.