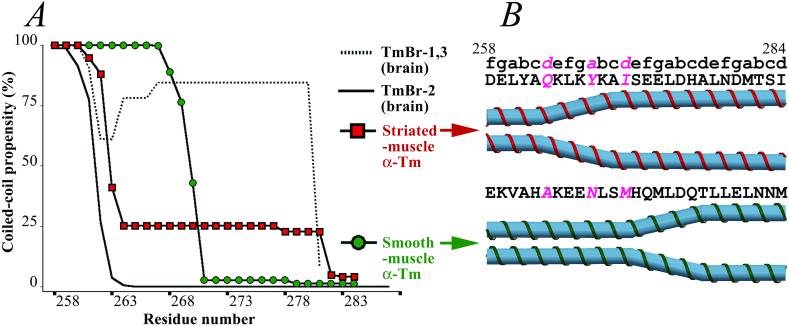
Figure 3.
Structural variations in the C-terminal region of different vertebrate Tm isoforms. (A) Coiled-coil predictions, using the program COILS (28–29) (with a 14-residue window size) for the C-terminal regions of the products of the α-Tm gene. In striated-muscle α-Tm, encoded by exon 9a (red squares), the coiled-coil propensity decreases sharply after Gln-263, consistent with a 22-residue splayed region observed in the current study (see Materials and Methods). Vertebrate smooth-muscle α-Tm and many nonmuscle isoforms, encoded by exon 9d (green circles), are also predicted to be α-helical but not in a two-stranded coiled-coil conformation at the C terminus. However, the coiled coil in these isoforms appears to extend beyond residue 262 to at least residue 270. In the brain isoforms, TmBr-1 and TmBr-3, encoded by exon 9c (dotted line), the C terminus is predicted to be an α-helical coiled coil to the very end. In another brain isoform, TmBr-2, encoded by exon 9b (solid line), the C-terminal region is mostly likely not α-helical because of three closely spaced prolines. (B) Schematic representation of the C-terminal ends of striated- and smooth-muscle α-Tms.