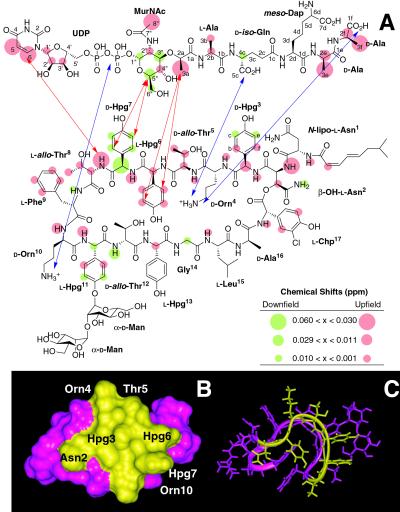
Figure 4.
(A) NMR localization of the binding interface between ramoplanin (1) and Park's nucleotide (6) (1:1 molar ratio). Protons that exhibit downfield chemical shifts on binding are colored green; those that shift upfield are depicted in orange. Protons that do not shift on binding are colorless. Intermolecular NOEs are depicted by red arrows. Possible anchoring electrostatic interactions between ramoplanin Orn4 and Orn10 residues and 6 are indicated by blue arrows. NMR experiments further localize the minimum PG structure recognized by ramoplanin to the intact pyrophosphate, the muramyl carbohydrate, and the first two amino acids of the pentapeptide. (B) Surface localization of the peptidoglycan monomer/lipid intermediate binding region of ramoplanin. Residues comprising the binding interface identified by NMR that lie on the same face of the antibiotic are colored yellow and mapped onto (C) the three-dimensional NMR structure of ramoplanin obtained in 20% DMSO (25).