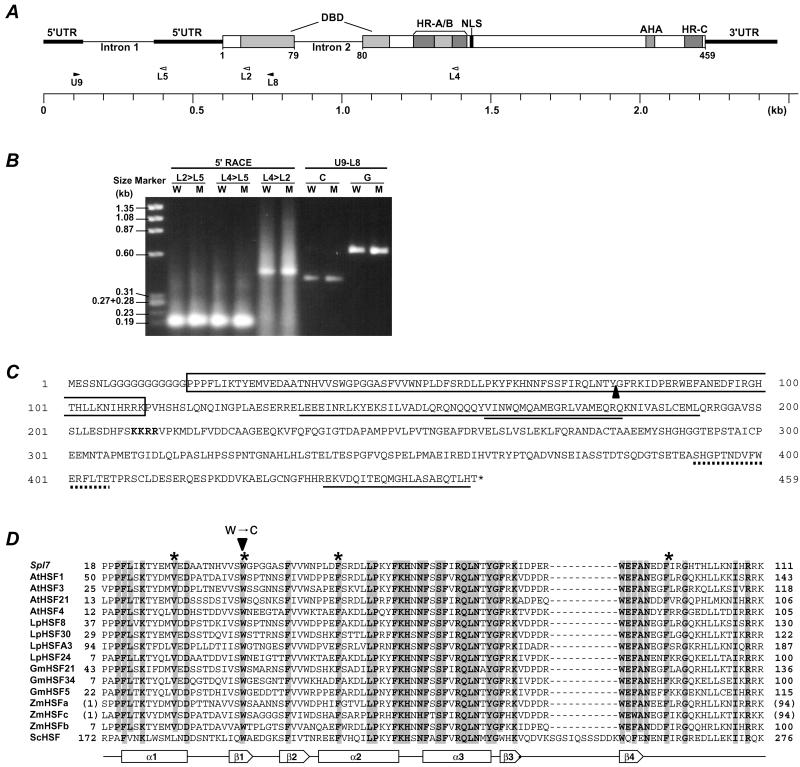
Figure 4.
The structure of Spl7. (A) The block diagram of the Spl7 structure indicates the position of the typical functional elements. The positions of the primers used for 5′ RACE-PCR are shown by white arrowheads, and those of the primers used for RT-PCR are shown by black arrowheads. (B) Gel blot of the PCR products. W shows wild-type template and M shows mutant template. L2>L5 means that 5′ RACE used the gene-specific primer L2 for the primary PCR and L5 for the nested PCR. U9-L8 shows that the PCR products used the primer combination U9 and L8. C and G show cDNA template and genomic DNA template, respectively. (C) The predicted amino acid sequence. The sequence is shown in single-letter code. The DBD is boxed and the position of intron 2 is shown by a black triangle. The nuclear localization sequence (NLS) is written in bold. The hydrophobic heptad repeat regions are single-underlined (HR-A/B amino acids 134–191, HR-C amino acids 438–458), and an insertion of 21 aa residues between HR-A and HR-B is double-underlined. The AHA is dot-underlined. (D) Alignment of deduced amino acid sequence of Spl7 and known HSF DBD regions. The numbers on both sides indicate the amino acid positions of each protein. Because ZmHSFa and ZmHSFc are partial cDNA clones of DBDs, the temporary amino acid positions are displayed in parentheses. Conserved amino acids among all of the plant HSFs listed here are shaded. The position of the amino acid substitution is shown by an arrowhead. The secondary structure elements based on the LpHSF24 crystal structure (51) are shown below the sequence alignment: α1 to α3, α-helix; β1 to β4, β-sheet. The putative amino acids constituting the central hydrophobic core of the tertiary structure are shown by asterisks.