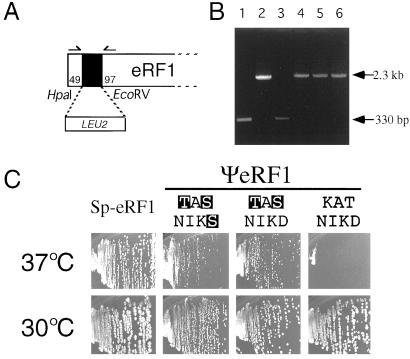
Figure 3.
The capacity of wild-type and variant ΨeRF1 proteins to complement the nullified eRF1 gene of S. cerevisiae. (A) The gene disruption of S. cerevisiae eRF1. The LUE2 marker was inserted into the HpaI-EcoRV sites of the SUP45 sequence cloned in plasmid pET-Sc-eRF1. Numbers refer to the initiator codon of the eRF1 gene. The DNA containing the nullified Δsup45∷LEU2 allele was amplified by PCR using multicloning site primers that flank the sup45 insert and transformed into MT557/1d (sup45 ts) cells in the presence of pYX112 plasmids encoding Sp-eRF1 and wild-type (KATNIKD) or variant (TASKINS and TASNIKD) ΨeRF1s; Leu+ (Ura+) transformants were selected, and those whose chromosomal copy of the eRF1 (sup45 ts) sequence was replaced by the Δsup45∷LEU2 allele were isolated. (B) DNA analyses of the disruption of chromosomal copy of eRF1 in S. cerevisiae transformants. The DNAs containing the insert were amplified from Leu+ transformants obtained in A by PCR using primers 5′-TATTGAGATCTGGAAGGTCAAGAAGTTGG-3′ and 5′-GTTGATAGGTTTGTAAGGTTCGATGTC-3′ shown by arrows in A. These two primer sequences were chosen from S. cerevisiae eRF1 and do not crossreact with Tetrahymena eRF1 or S. pombe eRF1 sequences. Samples used for PCR amplification: lane 1, plasmid DNA encoding the wild-type eRF1 of S. cerevisiae (control); lane 2, plasmid DNA encoding the Δsup45∷LEU2 eRF1 of S. cerevisiae (control); lanes 3–6, Leu+ transformant DNAs selected as in A, in which the chromosomal copy of eRF1 was (lanes 4–6) or was not (lane 3) disrupted by the LEU2 insert. Lanes 4, 5, and 6 represent Leu+ transformants expressing wild-type (KATNIKD) and variant (TASNIKS, TASNIKD) ΨeRF1 proteins, respectively. (C) The growth of the eRF1-nullified S. cerevisiae cells in the presence of plasmids encoding Sp-eRF1 and wild-type or variant ΨeRF1 proteins at 30°C and 37°C.