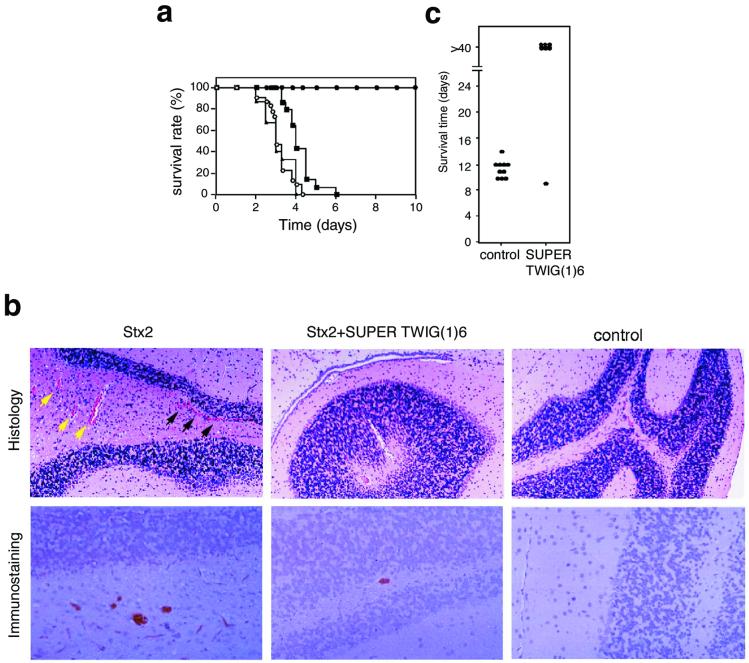
Figure 3.
Inhibitory effect of SUPER TWIG (1)6 on the lethality of Stx2 or infection with E. coli O157:H7 in mice. (a) A lethal dose of Stx2 (0.25 ng/g of body weight) was administered to mice without any SUPER TWIG (○; number of mice = 30) or with SUPER TWIG (0)3 (▴; number of mice = 15), (1)6 (●; number of mice = 20), or (1)12 (▴; number of mice = 14) (50 μg/g of body weight). Data represent the survival rate of each group. Data of the first 10 days are shown. (b) Histologic examination and immunostaining of Stx2 in the brain. Sections of cerebellar cortex were used for staining. For histologic examination, the sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (Upper). Black and yellow arrowheads indicate perivascular hemorrhage and congestion, respectively. Stx2 present in the sections was detected by using specific antibody against Stx2 (Lower). (×80.) (c) Mice with protein calorie malnutrition were infected intragastrically with E. coli O157:H7 strain N-9 (2 × 106 colony-forming units) on day 0. SUPER TWIG (1)6 (50 μg/g of body weight) or saline alone was administered intravenously to the mice (control, n = 10; SUPER TWIG-treated, n = 7) twice a day from day 3 to day 6. Data represent the survival time of each mouse.