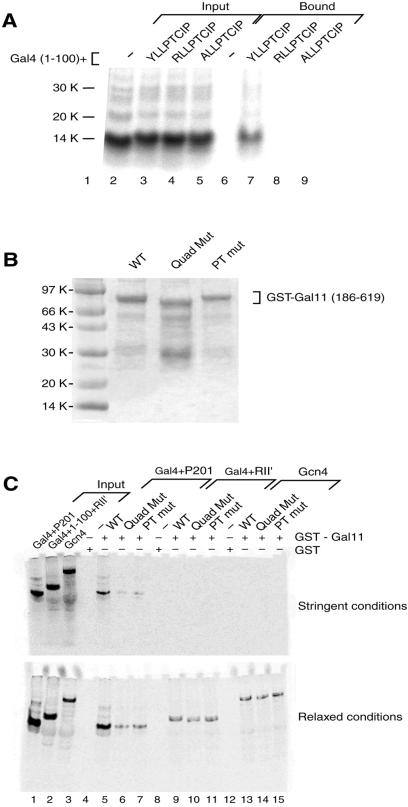
Figure 5.
Interaction between P201 and Gal11 in vitro. (A) Mutations in P201 abolish the interaction with Gal11(186–619) observed in a GST pull-down assay. Equal amounts of radiolabeled Gal4(1–100) and Gal4+P201 as well as two mutant derivatives of the latter, were tested for interaction with Gal11(186–619) in an in vitro pull-down assay. The Gal11 fragment was isolated as a GST-fusion protein, attached to beads, and incubated with radiolabeled Gal4 derivatives. Input lanes (2–5) contain 20% of the labeled activators incubated with the immobilized GST-Gal11. Bound lanes (6–9) show that only the derivative bearing wild-type P201 bound to Gal11 under these (stringent) conditions (see Materials and Methods). (B) Preparation of GST-Gal11 derivatives. Coomassie-stained gel showing the expression of three forms of GST-Gal11(186–619). The first lane shows the wild-type (WT) protein, the second lane shows the quadruple mutant (Quad Mut) of Fig. 3, and the third lane shows the T322K mutant (PT mut) form of the Gal11 fragment. As expected, the quadruple mutant, which includes the short deletion (residues 443–470), migrates slightly faster than the other two forms. (C) Mutations in Gal11 abolish the interaction with P201 observed in a GST pull-down assay. This experiment was performed as in A, except that various mutant versions of gal11 were tested for interaction with three activators. Input lanes (1–3) contain 20% of three radiolabeled activators used in the GST pull-down assay. Gal4(1– 100)+(840–881) is a weak acidic activator, and Gcn4 is the full-length form of another acidic yeast activator. Under stringent conditions (see Materials and Methods) the only activator that bound wild-type GST-Gal11(186–619) was Gal4+P201 (lane 5). That interaction was abolished by mutation of Gal11 (lanes 6 and 7). Under relaxed conditions, in addition to the strong interaction observed between wild-type Gal11 and Gal4+P201 (lane 5), a weaker interaction with either of the two mutant forms of Gal11 was observed (lanes 6 and 7). A weak interaction between Gal11 and the two other activators was observed also, but those interactions were unaffected by mutation of Gal11.