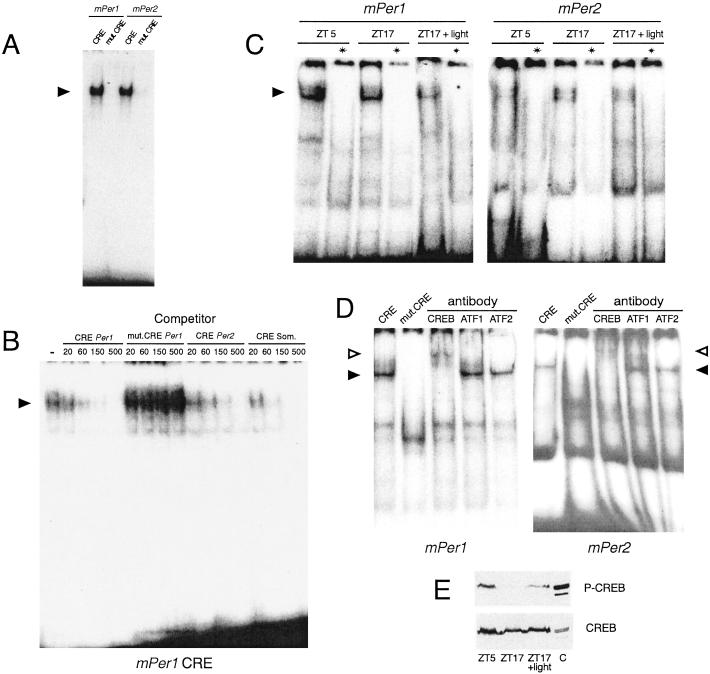
Figure 2.
Specific binding of CREB to wild-type CRE of mPer1 and mPer2 promoters. (A) Gel mobility-shift assay using wild-type or mutated mPer1 or mPer2 CRE oligonucleotides, plus bacterially expressed CREB protein. The specific complex is indicated by an arrowhead. (B) Competition gel mobility-shift assay using labeled mPer1 CRE oligonucleotide together with nuclear extract from Rat-1 fibroblasts. Competition is made by preincubating the labeled DNA with increasing amounts (20–500 ng) of unlabeled wild-type mPer1, mPer2, or somatostatin CRE or mutated mPer1 oligonucleotides. The specific complex is indicated by an arrowhead. (C) Gel mobility-shift assay using mPer1 or mPer2 CRE oligonucleotides along with nuclear extracts from the SCN of rats killed during the day (ZT5), and during the night (ZT17) either in the darkness or 1 h after the beginning of a 30-min light pulse. (D) Supershift assay on SCN nuclear extracts with mPer1 or mPer2 CRE after preincubation of SCN nuclear extract with anti-CREB, anti-ATF1, and anti-ATF2 antibodies. The specific complex is indicated by a closed arrowhead and the supershifted by an open arrowhead. The first lane is the control without antibody and the second lane is a complex with mutated oligonucleotide. (E) Immunoblotting of SCN protein extracts from rats killed as in C, with an anti-phosphorylated CREB (P-CREB) antibody. “C” is a control containing P-CREB (EGF-stimulated fibroblasts).