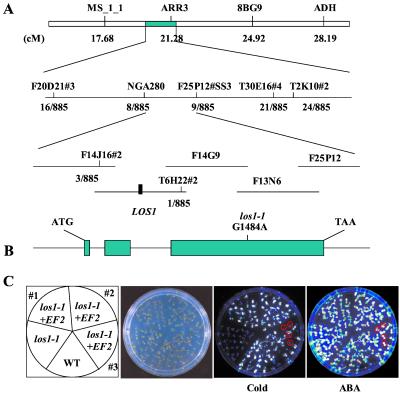
Figure 6.
Positional cloning of the LOS1 gene. (A) Genetic mapping delimited LOS1 to BAC clones F14J16 and T6H22. The los1–1 mutation was identified by sequencing and comparing all predicted genes on these BAC clones from los1–1 mutant and wild-type plants. (B) Structure of LOS1 and the position of the los1–1 mutation. Positions are relative to the translation initiation codon. Filled boxes indicate the ORF, and lines between boxes indicate introns. The G1484A mutation in the los1–1 mutant is indicated. (C) Complementation of los1–1 mutant by the wild-type (WT) LOS1 gene. Ten-day-old wild-type, los1–1, and two homozygous T3 progenies and one T2 progeny of the los1–1 plant containing the wild-type LOS1 (indicated as los1–1 + EF2) were assayed for complementation. From left, picture indicates the position of wild-type, los1–1, and the T3 (nos. 1 and 2) and T2 (no. 3) progenies; picture of the plants in an agar plate; luminescence image of the plants incubated at 0°C for 48 h; and luminescence image of the plants treated with 100 μM ABA for 3 h. los1–1 plants in the segregating T2 progeny (no. 3) were circled, which showed low luminescence in the cold but normal luminescence under ABA treatment.