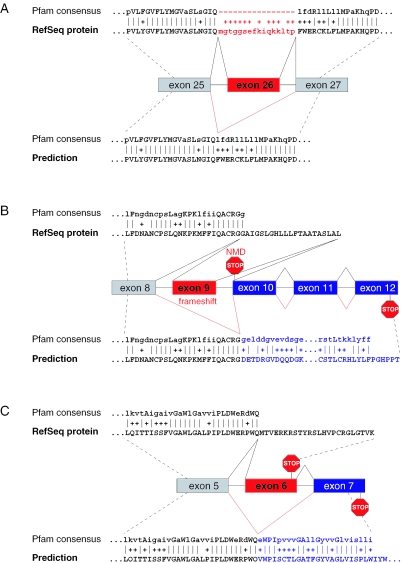
Figure 1.
Effect of alternative exons on Pfam domains. (A) SLC4A5 (NM_033323): exon 26 disrupts the Pfam domain PF00955 as shown by the gaps in the alignment. Skipping of the exon increases the Pfam score from 1183 to 1208. (B) CASP2 (NM_001224): inclusion of exon 9 results in a reading frame with a stop codon in exon 10 and this transcript should induce NMD. The skipping of exon 9 leads to a frameshift and a new C-terminal part of the Caspase domain PF00656 (score increase from 174 to 317). (C) PIGF (NM_173074): exon 6 encodes an in-frame stop codon 33 nt upstream of the last exon–exon junction which should not elicit NMD. Skipping of exon 6 results in a new C-terminus encoded by exon 7 and a score increase for PF06699 from 299 to 362. Alternative exons are depicted in red, exons that become coded in the predicted splice form are depicted in blue. Pfam alignments for the RefSeq protein are shown at the top, for the predictions at the bottom. All exon skipping events are supported by several ESTs.