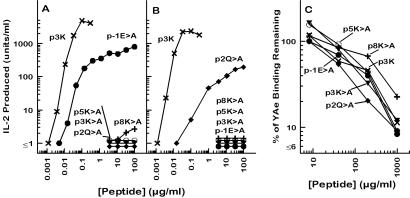
Figure 5.
p3K amino acids important for T cell recognition. The responses of two T cell hybridomas, B3K05-6 (A) and B3K05-8 (B), produced from T cells from p3K-immunized IAb mice (25), were tested for their responses to a set of p3K mutant peptides presented by the IAb-bearing cell line, LB-15.13 (35). The results are shown as the units of IL-2 produced vs. the concentration of peptide offered. (C) Spleen cells from IAb-bearing invariant chain knockout mice were incubated with pEα (20 μg/ml) for 4 h at 37°C. The level of binding of pEα to IAb was assessed by flow cytometry using the IAb/pEα-specific monoclonal antibody, YAe (24). Competition between pEα and p3K or its variants was assessed by the reduction in YAe staining when various concentrations of the competitor peptide were included in the incubation of the spleen cells with pEα. The results are shown as the percent of the mean fluorescence (corrected for autofluorescence) remaining measured with fluoresceinated YAe vs. the concentration of the competitor peptide. In all three panels the symbols are as follows: Unmutated p3K (×); p-1E>A (which indicates an E → A mutant) (●), p2Q>A (♦), p3K>A (▾), p5K>A (○), and p8K>A (+).