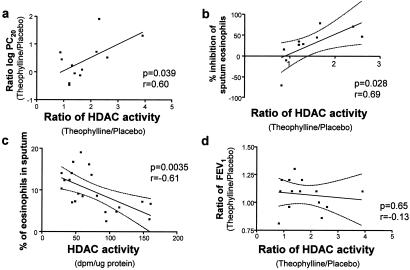
Figure 2.
Correlation between theophylline actions on HDAC activity and clinical parameters. (a and b) Correlation between changes in HDAC activity induced by theophylline and theophylline-induced changes in PC20 (concentration that provokes a 20% change in FEV) for methacholine (a) and inhibition of sputum eosinophils (b). (c) Correlation between HDAC activity and sputum eosinophils in normal and asthmatic subjects. (d) No correlation between FEV1 (forced expiratory volume in 1 s) and theophylline-induced HDAC activity. Dotted lines represent 95% confidence limits.