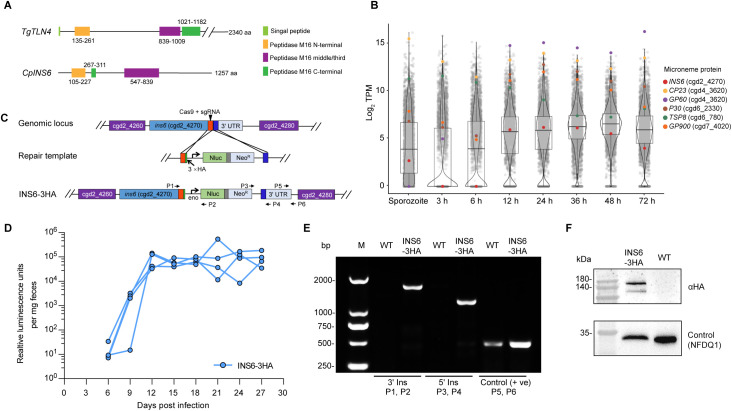
Fig 1. Endogenous epitope tagging of INS6.
(A) Schematic representation of the structural domains of INS6 and its homologue gene, toxolysin 4 (TLN4). Both INS6 and TLN4 have three structural domains associated with classical insulinase peptidase, including the M16 N-terminus, the M16 middle/third terminus, and the M16 C-terminus, in addition to a signal peptide in TLN4. (B) Violin plots demonstrate the transcript expression of C. parvum genes in sporozoites and different development stages of parasites grown on HCT-8 cells, as indicated by TPM values from RNA-seq analysis of the transcriptome. Colored dots represent microneme genes, with INS6 indicated in purple. (C) Schematic showing the tagging strategy of INS6 locus. The location of the sgRNA, Cas9 break site, and the repair template for homologous recombination are shown. 3 × HA, triple hemagglutinin epitope tag; Nluc, nanoluciferase; NeoR, neomycin resistance marker; Eno, enolase promoter. (D) Fecal luminescence measurements of mice infected with INS6-3HA sporozoites. Ifng−/− mice were infected with INS6-3HA electroporated sporozoites, relative luminescence was measured from feces after infection at indicated days. Each data point represents one mouse. In total, four mice were used in this experiment. (E) PCR analysis of INS6-3HA strain. Fecal genomic DNA from wild-type (WT) and INS6-3HA parasites were used as template, and primers for checking 5’ insertion (5’ Ins), 3’ insertion (3’ Ins), and the 3’ UTR sequence of INS6 as a positive control (+ve) are indicated in panel C. (F) Western blot analysis of INS6 expression in oocysts. INS6-3HA transgenic and WT oocysts were probed with anti-HA antibody (top panel) and a polyclonal antibody against the NFDQ1 as a loading control (bottom panel). NFDQ1 is a protein that contains the characteristic NFDQ amino acid repeat motifs [26].