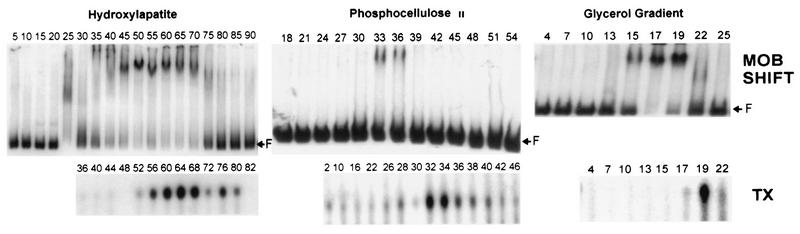
FIG. 4.
Electrophoretic mobility shift assays and specific transcription reactions of fractions from the purification of VLTF-X. (Top) Electrophoretic mobility shift assays (MOB SHIFT) with fractions from the hydroxylapatite, phosphocellulose II, and glycerol gradients used to purify VLTF-X (see Fig. 1). Reactions were conducted in 20-μl volumes, which contained approximately 1 ng of a 32P-labeled late promoter-containing fragment as described in Materials and Methods. Proteins used were 2 μl of fractions from the hydroxylapatite column, 4 μl of fractions from the phosphocellulose column, or 7 μl of fractions from the glycerol gradient. The reaction mixtures containing the hydroxylapatite fractions contained 50 ng of poly(dI-dC) · poly(dI-dC) as nonspecific competitor; the reaction mixtures containing the phosphocellulose and glycerol gradient fractions contained 10 ng of poly(dI-dC) · poly(dI-dC) as competitor. Fraction numbers are indicated above the lanes. F indicates the position of free probe. Autoradiograms of the gels are shown. (Bottom) Specific transcription reactions (TX) with fractions from the columns used to purify VLTF-X. Proteins used in transcription reactions were as follows: for the hydroxylapatite column, 1.7 μl of A1L protein, 2 μl of G8R protein, 2 μl of A2L protein, 2.5 μl of RNA polymerase purified from infected cells, and 5 μl of the indicated column fractions (numbers above the lanes); for the phosphocellulose column, 2 μl of A1L protein, 3 μl of G8R protein, 2 μl of A2L protein, 2 μl of RNA polymerase purified from infected cells, and 5 μl of the indicated column fractions; and for the glycerol gradient, 2 μl of A1L protein, 3 μl of G8R protein, 4 μl of A2L-GST fusion protein, 3 μl of RNA polymerase purified from infected cells, and 5 μl of the indicated column fractions. Autoradiograms of the gels are shown as described for Figure 2.