Fig 1.
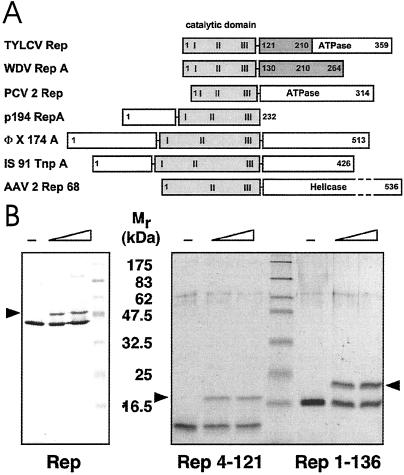
Domain organization and activity of Rep proteins. (A) Domain structure of TYLCV Rep, wheat dwarf virus (WDV) RepA, porcine circovirus 2 (PCV2) Rep, plasmid pC194 RepA, bacteriophage ΦX174 A, transposon IS91 TnpA, and AAV2 Rep68 proteins. The catalytic domains are displayed in gray, and the conserved sequence motifs (28) are labeled I, II, and III. The oligorimerization domains of TYLCV Rep and WDV RepA are shown in dark gray. (B) Activity assays of TYLCV Rep proteins. (Left) Western blot analysis of a 12% denaturing gel. (Right) A 15% gel after Coomassie staining. About 20–40% of Rep becomes covalently linked to the 5′ end of the 15-nt cleavage product (marked by arrow) under these conditions. The sizes of molecular weight markers are indicated between the panels.